apparent power
What is apparent power?
Apparent power is a measure of alternating current (AC) power that is computed by multiplying the root-mean-square (rms) current by the root-mean-square voltage. In a direct current (DC) circuit, or in an AC circuit whose impedance is a pure resistance, the voltage and current are in phase, and the following formula holds:
P = ErmsIrms
In this formula, P is the power in watts, Erms is the rms voltage in volts, and Irms is the rms current in amperes. However, in an AC circuit, impedance consists of reactance as well as resistance. As a result, the voltage and current are not in phase. This complicates the determination of power.
How does apparent power compare to true and reactive power?
In an AC circuit, the product of the rms voltage and the rms current is called apparent power. When the impedance is a pure resistance, the apparent power is the same as the true power. But when reactance exists, the apparent power is greater than the true power.
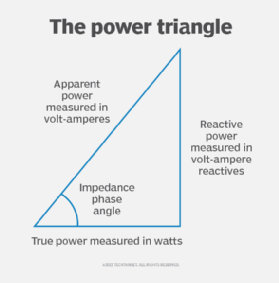
The vector difference between the apparent and true power is called reactive power, which is measured in terms of volt-amperes reactive, or VAR. Reactive power is energy that is stored and then released as a magnetic field in the case of an inductor and an electrostatic field in case of a capacitor.
If Pa represents the apparent power in a complex AC circuit, Pt represents the true power, and Pr represents the reactive power, then the following equation holds:
Pa2 = Pt2 + Pr2
How does apparent power differ from active power?
Apparent power is the total power that's available to run a computer, illuminate a lightbulb and power a manufacturing system.
If all the available power isn't used, the active power, or real power, is the power that is actually used for a specific load. This is important because it is the active power that is used by power companies and is what customers pay for on their bills.
The ratio of the active power to the apparent power is referred to as the power factor. It is a number between 0.0 and 1.0.
Comparing the volt-ampere and watt
Volt-amperes (VA) and watts (W) are used to measure power in an electrical circuit. Both are used in DC and AC systems. In DC circuits, the W and VA values are usually equal. In AC systems, the W and VA values may be different. The former indicates "true power" and the latter indicates "apparent power."
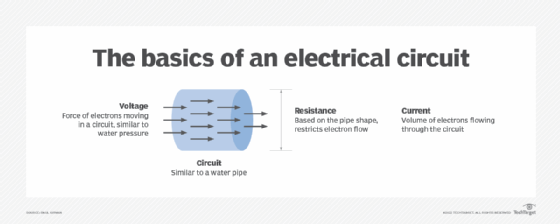
VA denotes the energy consumption of an electrical device, that is, how much current the device consumes when in use. It is measured by multiplying the volts (V) and amperes (A). Volts define the electromotive force that pushes electrons through a circuit. Amperes measure the flow -- or current -- of electrons in a circuit. Resistance is something that restricts or slows the flow of electrons.
Applications of apparent power and volt-amperes
Energy efficiency is a key goal in many organizations and especially in data centers, which are heavy consumers of electrical power. When determining the power attributes and requirements of a data center, knowledge of VA and apparent power is important.
VA helps simplify calculation of power use, which then is used to determine the power supplies, circuit breakers and other power management components.
Apparent power is useful when calculating the size of an uninterruptible power supply (UPS), for example. When sizing a UPS, knowledge of the power requirements of various devices, such as servers, laptops and heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems, is necessary, as is knowledge about the overall data center.
Energy efficiency is a critical part of building and running a data center. Find out six energy-efficient best practices.
