henry (H)
What is a henry?
The henry (symbolized H) is the International System of Units (SI) derived unit of electrical inductance. Reduced to base SI units, one henry is the equivalent of one kilogram meter squared per second squared per ampere squared (kg m2 s-2 A-2).
In a circuit where the current is changing at a constant rate of one ampere per second (A/s), an inductance of 1 H results in the generation of one volt (V) of potential difference across an inductor. More rapid current changes produce much greater surges of electromotive force (emf). This is the principle by which a spark coil generates a high and dangerous voltage.
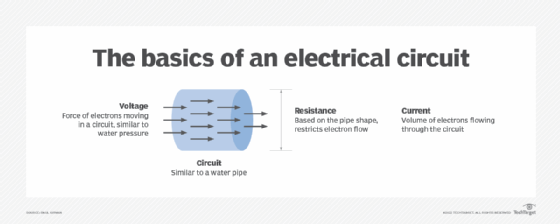
How is the henry used?
As the SI unit of inductance, the henry is a large unit. In audio frequency and radio frequency applications, common units include the following:
- millihenry (mH), where 1 mH = 10-3 H
- microhenry (µH), where 1 µH = 10-6 H
The filter choke in a power supply is a field coil designed to produce a large voltage upon release of its stored magnetic energy. Occasionally, a field coil will be found whose value can be expressed in henries. In very high frequency, ultrahigh frequency and microwave devices and systems, units used include:
- nanohenry (nH), where 1 nH = 10-9 H
- picohenry (pH), where 1 pH = 10-12 H
What is inductance?
Because henries are the measure of inductance, understanding inductance is useful. American scientist Joseph Henry (1797-1878) and British scientist Michael Faraday (1791-1867) discovered and defined electromagnetic induction around the same time.
Inductance is a property of a conductor, such as a copper wire twisted into a coil. It's measured by the voltage, or emf, induced in it. Changes that occur in the electric current producing the voltage affect inductance.
An unchanging current produces a steady magnetic field around the coil. By contrast, when a varying current, such as alternating current, is present, a variable magnetic field strength results. This generates an emf in the conductor.
As the current varies, so does the emf per voltage in proportion to the change rate of the current. Inductance is determined by obtaining the emf value induced in the conductor and dividing it by amount of the change rate of current causing the induction.
Several factors affect the inductance of a coil, including the following:
- how many times the conductor is coiled;
- the physical length of the coil;
- what is used to make up the coil's core; and
- the number of layers in which the coil is wound.
Self-induction vs. mutual induction
Two variants of induction can be observed. Self-induction occurs when a conductor that is transporting varying current generates a varying magnetic field. This approach induces another emf on the same conductor. Examples are traffic signal sensors that identify when a vehicle approaches an intersection and metal detectors that screen for the presence of metal when someone walks through them.
This contrasts with mutual induction, where a secondary conductor is present that generates its own emf and is different from the primary conductor transporting varying current. The secondary conductor induces an emf on the primary conductor. Transformers, electric motors, metal detectors and radio receivers are examples of mutual induction.
Learn about electrical safety in the data center, including identifying and dealing with hazards.
