fan-out
What is fan-out?
In digital circuitry, fan-out is a measure of the maximum number of digital inputs that the output of a single logic gate can feed without disrupting the circuitry's operations. Most transistor-to-transistor logic (TTL) gates can support up to 10 other digital gates or devices. Thus, a typical TTL gate has a fan-out of 10. In contrast, complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) gates can support over 50 connected devices, giving them a fan-out rate of greater than 50.
A logic gate can support only a specific number of connected devices, based on the gate's source and sink output currents, as well as the input requirements of the connected devices. The output current must be enough to meet the total needs of all the connected input devices. Exceeding the fan-out by adding too many devices can result in performance and reliability issues which may lead to data errors.
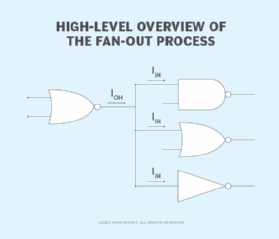
Figure 1 provides a high-level overview of the fan-out process. The logic gate on the left (in this case, an NOR gate) fans out to three other gates (NAND, NOR and NOT, from the top down). The IOH arrow indicates the high-level output current, and the IIH arrow indicates the high-level input current. The total IIH of all three input devices should not exceed the source device's IOH.
In some digital systems, it might be necessary to connect a single logic gate to more devices than are supported by the fan-out capacity. In those situations (see figure 2), a digital buffer can be used between the source logic gate and the connected devices. The buffer receives its input from the source gate and outputs the signal to the other devices, as shown in figure 2.
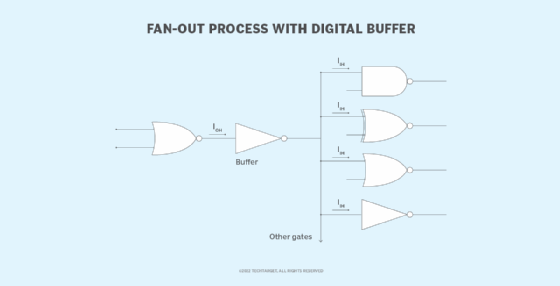
The buffer does not perform any inversions like a logic gate but it does provide digital amplification and helps to prevent impedance, making it possible to exceed the original number of supported devices. For example, a buffer could be used to fan out a TTL gate to 25 to 30 other devices, rather than the customary 10.
Instead of a buffer, two NOT logical gates can be used to create a double inversion that achieves similar results as a buffer, as illustrated in figure 3. Unlike the buffer, however, the two NOT gates convert the input signal from the source gate, rather than simply passing the signal along. Most digital circuits support this approach.
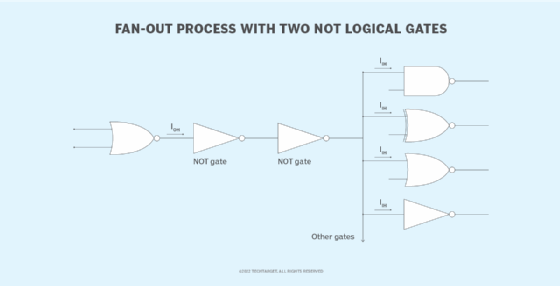
In this configuration, the first NOT gate (on the left) inverts the input signal to a different polarity. The second NOT gate then converts the signal back to its original state and outputs the signal to the other devices. Although this might seem an unnecessary procedure, given that the signal is returned to its original state, this process will actually amplify the signal, making it possible to exceed the original fan-out capacity.
The converse of fan-out is fan-in in which allows a circuit to support a number of digital inputs going into a single logic gate.
See also: integrated circuit, quad gates, transistor, Karnaugh map.
