core banking system
What is a core banking system?
A core banking system is the software that banks use to manage their most critical processes, such as customer accounts, transactions and risk management. It is the central nervous system of a bank, and it is essential for providing a seamless customer experience (CX) and maintaining compliance with regulations.
A core banking system typically includes the following modules:
- Accounting. This module tracks all a bank's financial transactions, including deposits, withdrawals, loans and payments.
- Customer relationship management (CRM). The CRM module helps banks manage their relationships with customers by storing customer data, tracking interactions and generating reports.
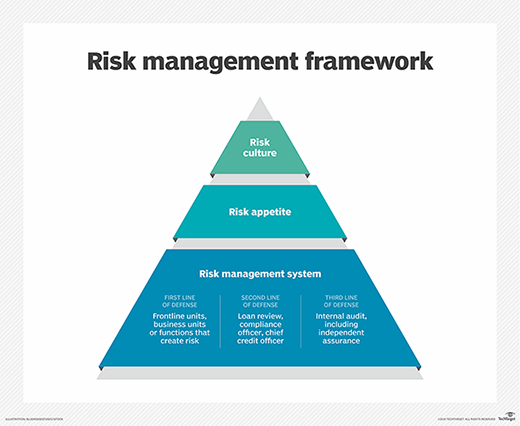
- Risk management. This module helps banks identify and mitigate risks, such as fraud and credit risk.
- Operations. This module supports day-to-day operations, such as processing transactions and managing accounts.
- Reporting. This module generates reports that help banks track performance and make decisions.
Core banking systems can be either on premises or cloud-based. On-premises systems are installed and maintained on the bank's own servers, while cloud-based systems are hosted by a third-party provider.
There are many different core banking systems available, and the best choice for a particular bank depends on its size, needs and budget. Some of the most popular core banking systems are the following:
- Finacle. This system is developed by Infosys and is used by over 1 billion customers in over 100 countries.
- Oracle Banking Cloud Services. This system is developed by Oracle and is used by over 130 banks in over 70 countries.
Core banking systems are a critical part of any bank's operations. By choosing the right system and implementing it effectively, banks can improve their efficiency, reduce costs and provide better CX.
Benefits of a core banking system
There are many benefits to using a core banking system, including the following:
- Improved efficiency. Core banking systems can help banks automate many of their manual processes.
- Reduced risk. Core banking systems can help banks identify and mitigate risks, such as fraud and credit risk.
- Enhanced CX. Core banking systems can help banks provide more seamless CX by making it easier for customers to manage their accounts and transactions.
- Increased compliance. Core banking systems can help banks comply with regulations by providing a central repository for all of their financial data.
Challenges of implementing a core banking system
There are also some challenges to implementing a core banking system, including the following:
- Cost. Core banking systems can be expensive to purchase and implement.
- Complexity. Core banking systems are complex pieces of software, and it can be difficult to implement them effectively.
- Integration. Core banking systems need to be integrated with other systems, such as the bank's CRM system and its risk management system. This can be a complex and time-consuming process.
Core banking systems are a critical part of any bank's operations. By choosing the right system and implementing it effectively, banks can improve their efficiency, reduce costs and provide better CX.
Learn about the top five benefits of AI in banking and finance, and see what developers need to know about open banking.
