end of life (EOL)
What is end of life (EOL)?
End of life (EOL), in the context of manufacturing and product lifecycles, is the final stages of a product's existence. In software applications, it means that the app has reached the end of its useful life. It may mean that a new version is available that supersedes the existing product. Or it may mean end of support (EOS), and the vendor no longer provides updates, patches and new features.
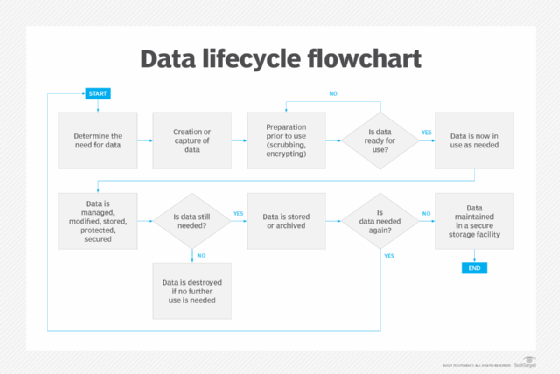
In the case of data, end of life refers to when it expires and is discarded or destroyed.
EOL concerns depend on the product itself and whether the perspective is that of the manufacturer or the user. For manufacturers, EOL concerns involve discontinuing production, while continuing to address the market needs that the product addresses. This can lead to new product development. For customers, EOL concerns include disposing of the existing product responsibly, transitioning to a different product and ensuring that disruptions are minimal.
What are indications of EOL?
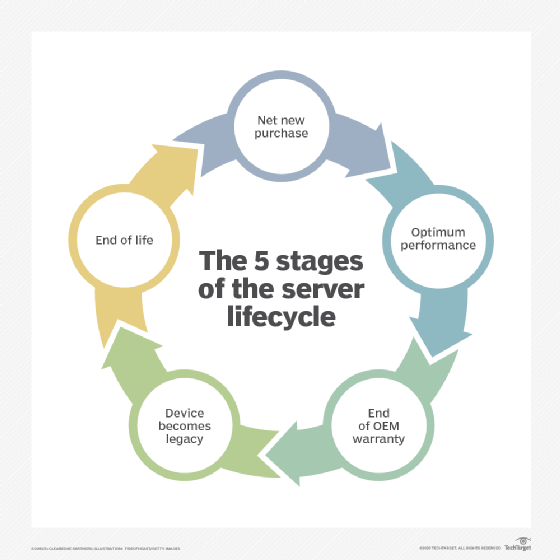
When dealing with PCs, servers, storage devices and other hardware end of life, IT professionals look for slow performance, files opening slowly, slow response when accessing a website, frequent crashing and similar issues. These indicate a device has reached EOL and should be replaced. IT pros often base these EOL product decisions on specific performance and warranty criteria their organization sets to determine when to replace a device.
Software applications that don't execute as they originally did or execute too slowly to be an effective business tool are candidates for replacement. Compatibility is also an issue; if an application doesn't operate on newer hardware or operating systems (OSes), replacement might be needed. A newer version of the app or a replacement application is the likely fix. If the application has reached its EOL and the vendor no longer provides software updates or support to the app, it may be at risk for a security breach.
EOL vs. EOS
End of life and end of support work in tandem in hardware and software lifecycles, with EOS often superseding EOL.
End of support
EOS is often the precursor to EOL. Manufacturers often announce an end date after which they no longer support a system or device. When they do this, they're often trying to migrate users to newer, and sometimes more expensive, versions of the older systems.
Hardware and software vendors have used this strategy for decades. For example, IBM would announce a new device to supersede an older system. The company typically also announced a date when technical support for the older device would no longer be performed. This was also true for IBM OSes and applications. Users effectively had no choice and acquiesced to the changes. This still occurs today, with vendors, such as Apple, Cisco and Microsoft, announcing EOS dates. Where the sale of a product is at issue, vendors refer to the end-of-sale date.
End of life
EOL is analogous to a product's end of service life (EOSL). This means the item no longer performs as it used to and should be taken out of service. Sometimes, a device that's designated as EOSL might be repurposed into something else. For example, a processor can be repurposed for a noncritical application. As such, EOSL precedes end of life dates because the device or system isn't officially at its EOL date but might be getting close.
How does PLM affect EOL?
Product lifecycle management (PLM) is a systematic approach to managing the series of changes a product goes through from its design and development to its ultimate retirement or disposal.
PLM software automates the management of product-related data, integrating it with other business processes, such as enterprise resource planning and manufacturing execution systems. Similar systems are used for IT hardware and software.
Establishing an EOL policy
To ensure that an organization is prepared when hardware and software have reached a point where they're no longer usable, it makes sense to establish an end-of-life policy. This can be part of an overall system or data lifecycle management policy.
The following are often included in an EOL policy:
- Guidance on determining when equipment can no longer be effectively maintained.
- Cost-benefit decisions regarding acquiring newer equipment.
- Options for device reuse, repurposing or donation.
- Disposal techniques that are consistent with sustainable environment practices.
Managing PC and desktop lifecycles includes EOL decisions. Find out how comprehensive device-as-a-service plans work, as well as full in-house management.
