red teaming
What is red teaming?
Red teaming is the practice of rigorously challenging plans, policies, systems and assumptions by adopting an adversarial approach. A red team may be a contracted external party or an internal group that uses strategies to encourage an outsider perspective.
The goal of red teaming is to overcome cognitive errors such as groupthink and confirmation bias, which can impair the decision-making or critical thinking ability of an individual or organization.
A red team is often a group of internal IT employees used to simulate the actions of those who are malicious or adversarial. From a cybersecurity perspective, a red team's goal is to breach or compromise a company's digital security. A blue team, on the other hand, is a group of internal IT employees used to simulate the actions of individuals within a given company or organization, often a security team. If the red team poses as a group of cybercriminals, the blue team's goal is to stop them from committing a hypothetical data breach. This type of interaction is what is known as a red team-blue team simulation.
Red teaming, however, does not exclusively require the existence of a blue team. In fact, this can often be a purposeful decision to compare the active and passive systems of an agency.
Red teaming originated in the military to realistically evaluate the strength and quality of strategies by using an external perspective. Since then, red teaming has become a common cybersecurity training exercise used by organizations in the public and private sectors. Other security testing methods include ethical hacking and penetration testing, or pen testing. While the red team shares the same goal and perspective of these strategies, their execution is often quite different.
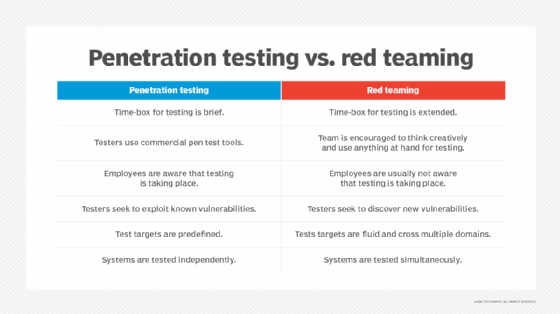
Penetration testing vs. red teaming
Pen testing and red teaming are often used interchangeably to describe security testing techniques. Each uses an "outside" perspective but does so in a different way.
Penetration testing
Pen testing is a manual security testing method that organizations use to provide a comprehensive overview of the quality and effectiveness of their security controls. The goal is to test the vulnerability of networks, assets, hardware, platforms and applications within a defined scope.
Unlike a vulnerability assessment -- an evaluation process used to rank cybersecurity weaknesses in order of importance and/or risk -- pen testing uses the effort of ethical hackers to physically and virtually challenge the strength of IoT devices. These tests are deliberate and meticulous, placing no focus on stealth or evasion. The main reason for this is that pen testing distinctively lacks a respective competing blue team. In fact, the blue team is often made aware of the scope and depth of the penetration test being conducted.
Learn the necessary steps for network penetration testing.
Red teaming
Red teaming is a stealthy procedure that often aims to test not only the systems and protocols in place, but also the people who manage them. Red teaming is a focused, goal-oriented security testing method that is designed to achieve specific objectives. If the objective of a red team is to access a sensitive server or a business-critical application, its success will be measured by how well it can accomplish this objective. If the red team achieves its goal, then the organization is insufficiently prepared to prevent such an attack.
The lack of notice is what distinguishes red teaming from pen testing. Blue teams are often purposely left in the dark during these evaluations. The goal of this is to force the blue team to respond as if it were an actual attack, providing a more accurate assessment.
Read more here about penetration testing vs. red teaming.
Red team methodology
Red teaming involves a very tactical and deliberate process to extract all of the desired information. However, to ensure the measurability and control of the procedure, an assessment must be completed prior to the simulation. This assessment should aim to use the mindset and goals of legitimate cybercriminals to identify entry points and vulnerabilities that one wishes to exploit.
The information gathered from this examination is essential to formulating goals the red team wants to achieve. If the red team finds a weakness associated with digital assets, physical assets, technical processes or operational processes, the red teaming session will aim to prioritize its exploitation.
Once the objectives have been determined, the red team will initiate an attack. Typically, the blue team will be able to identify the activity of the red team as malicious and start to contain or limit the success of their efforts. After the exercise is complete, each party will provide a list of findings that showcase the value of their perspective -- and the exercise as a whole.
The blue team will identify any indicators of compromise (IoC) that they were able to detect during the engagement. IoCs are flags that security teams use to register suspicious activity. On the other side, the red team will prepare a breakdown of its tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) for the blue team.
Together, the two teams use the results to create a list of actionable items -- such as firewall upgrades or server configurations -- that they can perform to improve the detection and response activity of the current security system.