graphics processing unit (GPU)
What is a graphics processing unit (GPU)?
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a computer chip that renders graphics and images by performing rapid mathematical calculations. GPUs are used for both professional and personal computing. Originally, GPUs were responsible for the rendering of 2D and 3D images, animations and video, but now they have a wider use range.
Like a central processing unit (CPU), a GPU is also a chip component in computing devices. One important difference, though, is that the GPU is specifically designed to handle and accelerate graphics workloads and display graphics content on a device such as a PC or smartphone.
An electronic device with an embedded or discrete GPU can smoothly render 3D graphics and video content, making it suitable for gaming and other visual applications. Over time, technological improvements have resulted in more flexible and programmable GPUs that can be used for many more applications and workloads other than gaming. GPUs are now used for creative content production, video editing, high performance computing (HPC) and artificial intelligence (AI).
What does a GPU do?
In the early days of computing, the CPU performed the calculations required for graphics applications, such as the rendering of 2D and 3D images, animations and video. As more graphics-intensive applications were developed, however, their demands put a strain on the CPU and decreased the computer's overall performance.
GPUs were developed as a way to offload those tasks from CPUs for graphics applications. A GPU performs graphics-related calculations very quickly and in parallel to allow for fast and smooth rendering of content on the computer screen. Since the GPU takes care of the calculations, the CPU is free to handle everything else that's not related to the graphics application.

How does a GPU work?
GPUs work by using a method called parallel processing, where multiple processors handle separate parts of a single task. A GPU will also have its own RAM to store the data it is processing. This RAM is designed specifically to hold the large amounts of information coming into the GPU for highly intensive graphics use cases.
For graphics applications, the CPU sends instructions to the GPU for drawing the graphics content on screen. The GPU executes the instructions in parallel and at high speeds to display the content on the device -- a process known as the graphics or rendering pipeline.
GPU use cases: What GPUs are used for today
GPUs are widely used for PC gaming, allowing for smooth, high-quality graphics rendering. Modern GPUs are also adapted to a wider variety of tasks than they were originally designed for, partially because they are more programmable than they were in the past. That's why GPUs are now also used to accelerate AI workloads and for machine learning (ML).
Some of the most popular applications of GPUs include the following:
- Accelerating the rendering of real-time 2D and 3D graphics applications.
- Video editing and video content creation.
- Video game graphics.
- Accelerating ML applications such as image recognition and facial detection and recognition.
- Training deep learning neural networks.
In recent years, GPUs have also been used to mine bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum. GPUs can perform the high-speed, parallel mathematical calculations required for crypto mining -- something that regular laptops with regular CPUs just cannot do.
Types of GPUs
Generally, there are two types of GPUs:
Integrated GPUs. An integrated GPU is built into the computer's motherboard. It could also be integrated with the CPU. Systems with integrated GPUs are generally small and light, since less space is required to incorporate the GPU.
GPU integration reduces the system's power consumption. In many cases, it also reduces the device's cost. That said, a laptop PC with an integrated GPU often is not upgradable, so if graphics needs change, it might require investing in an entirely new device.
Today, gaming laptops are available that align with modern games' system requirements, including GPU type and speed. These laptops smoothly render the graphics for different kinds of games and enhance gamers' playing experiences.
Discrete GPUs. A discrete -- or dedicated -- GPU can be mounted on a separate circuit board. It usually exists in the form of a removable graphics card with powerful capabilities for resource-intensive, high-performance applications such as 3D games.
A discrete GPU adds more processing power to the computer and can be upgraded as the user's needs change. However, it consumes more energy than an integrated GPU. It also generates considerable heat and will likely require dedicated cooling to reduce the heat and maximize GPU -- and laptop -- performance.
What is a cloud GPU?
In recent years, cloud GPU has emerged as an alternative to traditional GPU deployments.
A cloud GPU is suitable for companies that require heavy computing power or need to work with machine learning or 3D visualizations. A cloud GPU is a cloud-based GPU service or virtual GPU that removes the need to deploy a GPU or associated hardware and software on a local device.
Hosting GPUs in the cloud can have the benefits of freeing up local resources, saving time and cost, and providing greater scalability. Users can choose between a range of GPU types while gaining flexible performance based on their needs.
Furthermore, users can access cloud GPUs on demand from a web browser for a wide range of applications, including 3D rendering, training of ML models, gaming, medical imaging, financial risk management, generative AI, HPC and data analysis.
Many cloud service providers, including Google, provide cloud GPUs. Google Cloud offers high-performance GPUs for many applications. A range of GPU types are available that are suitable for a variety of workloads, budgets and performance requirements.
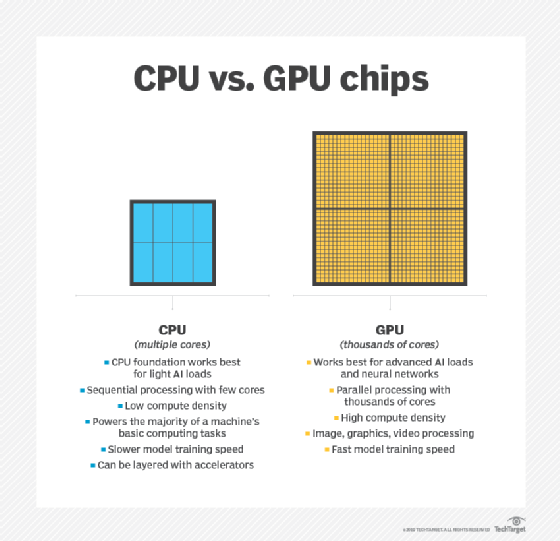
GPU vs. CPU
A GPU might be found integrated with a CPU on the same electronic circuit -- on a graphics card or in the motherboard of a PC or server. GPUs and CPUs are fairly similar in construction. However, CPUs are used to respond to and process the basic instructions that drive a computer, while GPUs are designed specifically to quickly render high-resolution images and video.
Essentially, CPUs are responsible for interpreting most of a computer's commands, while GPUs perform more complex mathematical and geometric calculations to focus on graphics rendering and other applications that require intensive calculations.
Both processors are available with different numbers of cores and transistors. The core can be thought of as the processor within the processor. Each core can process its own tasks, or threads. A CPU uses fewer cores and performs tasks sequentially. A GPU, in contrast, might have hundreds or thousands of cores, which allow for parallel processing and lightning-fast graphics output.
A single-core CPU usually does not have the capability for parallel processing, but multicore processors can perform calculations in parallel by combining more than one CPU onto the same chip. GPUs can also contain more transistors than a CPU.
In addition, a CPU has a higher clock speed, meaning it can perform an individual calculation faster than a GPU, so it is often better equipped to handle basic computing tasks.
Are GPUs and graphics cards the same?
GPU and graphics card are two terms that are sometimes used interchangeably. However, there are some important distinctions between the two. The main difference is that the GPU is a specific unit within a graphics card. The GPU is what performs the image and graphics processing. The graphics card is what presents images to the display unit.
Explore how CPUs, GPUs and DPUs differ from one another and what GPUs do in a data center.