text mining (text analytics)
What is text mining (text analytics)?
Text mining is the process of exploring and analyzing large amounts of unstructured text data aided by software that can identify concepts, patterns, topics, keywords and other attributes in the data. It's also known as text analytics, although some people draw a distinction between the two terms; in that view, text analytics refers to the application that uses text mining techniques to sort through data sets.
Text mining has become more practical for data scientists and other users due to the development of big data platforms and deep learning algorithms that can analyze massive sets of unstructured data.
Mining and analyzing text helps organizations find potentially valuable business insights in corporate documents, customer emails, call center logs, verbatim survey comments, social media posts, medical records and other sources of text-based data. Increasingly, text mining capabilities are also being incorporated into AI chatbots and virtual agents that companies deploy to provide automated responses to customers as part of their marketing, sales and customer service operations.
How text mining works
Text mining is similar in nature to data mining, but with a focus on text instead of more structured forms of data. However, one of the first steps in the text mining process is to organize and structure the data in some fashion so it can be subjected to both qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Doing so typically involves the use of natural language processing (NLP) technology, which applies computational linguistics principles to parse and interpret data sets.
The upfront work includes categorizing, clustering and tagging text; summarizing data sets; creating taxonomies; and extracting information about things like word frequencies and relationships between data entities. Analytical models are then run to generate findings that can help drive business strategies and operational actions.
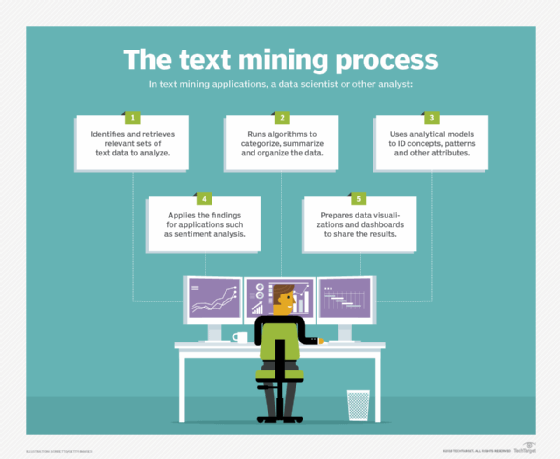
Key steps in text mining applications
In the past, NLP algorithms were primarily based on statistical or rules-based models that provided direction on what to look for in data sets. In the mid-2010s, though, deep learning models that work in a less supervised way emerged as an alternative approach for text analysis and other advanced analytics applications involving large data sets. Deep learning uses neural networks to analyze data using an iterative method that's more flexible and intuitive than what conventional machine learning supports.
As a result, text mining tools are now better equipped to uncover underlying similarities and associations in text data, even if data scientists don't have a good understanding of what they're likely to find at the start of a project. For example, an unsupervised model could organize data from text documents or emails into a group of topics without any guidance from an analyst.
Applications of text mining
Sentiment analysis is a widely used text mining application that can track customer sentiment about a company. Also known as opinion mining, sentiment analysis mines text from online reviews, social networks, emails, call center interactions and other data sources to identify common threads that point to positive or negative feelings on the part of customers. Such information can be used to fix product issues, improve customer service and plan new marketing campaigns, among other things.
Other common text mining uses include the following:
- Screening job candidates based on the wording in their resumes.
- Blocking spam emails.
- Classifying website content.
- Flagging insurance claims that may be fraudulent.
- Analyzing descriptions of medical symptoms to aid in diagnoses.
- Examining corporate documents as part of electronic discovery processes.
Text mining software also offers information retrieval capabilities akin to what search engines and enterprise search platforms provide, but that's usually just an element of higher-level text mining applications, and not a use in and of itself.
Chatbots answer questions about products and handle basic customer service tasks; they do so by using natural language understanding (NLU) technology, a subcategory of NLP that helps the bots understand human speech and written text so they can respond appropriately.
Natural language generation (NLG) is another related technology that mines documents, images and other data, and then creates text on its own. For example, NLG algorithms are used to write descriptions of neighborhoods for real estate listings and explanations of key performance indicators tracked by business intelligence systems.
Benefits of text mining
Using text mining and analytics to gain insight into customer sentiment can help companies detect product and business problems and then address them before they become big issues that affect sales. Mining the text in customer reviews and communications can also identify desired new features to help strengthen product offerings. In each case, the technology provides an opportunity to improve the overall customer experience, which will hopefully result in increased revenue and profits.
Text mining can also help predict customer churn, enabling companies to take action to head off potential defections to business rivals, as part of their marketing and customer relationship management programs. Fraud detection, risk management, online advertising and web content management are other functions that can benefit from the use of text mining tools.
In healthcare, text mining may be able to help diagnose illnesses and medical conditions in patients based on the symptoms they report.
Text mining challenges and issues
Text mining can be challenging because the data is often vague, inconsistent and contradictory. Efforts to analyze it are further complicated by ambiguities that result from differences in syntax and semantics, as well as the use of slang, sarcasm, regional dialects and technical language specific to individual vertical industries. As a result, text mining algorithms must be trained to parse such ambiguities and inconsistencies when they categorize, tag and summarize sets of text data.
In addition, the deep learning models used in many text mining applications require large amounts of training data and processing power, which can make them expensive to run. Inherent bias in data sets is another issue that can lead deep learning tools to produce flawed results if data scientists don't recognize the biases during the model development process.
There's also a lot of text mining software to choose from. Dozens of commercial and open source technologies are available, including tools from major software vendors, including IBM, Oracle, SAS, SAP and Tibco.







