PC card
What is a PC card?
A PC card, also known as a PCMCIA card, is a credit card-sized memory or input/output (I/O) device that fits into a PC, usually a laptop. Developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association, a PC card adds peripheral capability to a laptop. In this sense, it is an expansion card.
The PC card is not to be confused with another credit card-sized electronic card, the smart card, which contains an embedded microprocessor and memory, and is commonly used to authenticate users for a wide range of applications.
In the 1990s, the PC card added peripheral functionality to laptop computers, similar to what plugin boards did for desktops. The card was a plugin module containing a peripheral device, such as a modem, network adapter or storage drive. Although originally developed for use with many devices, including digital cameras, PC cards were most frequently used with laptop computers as many were equipped with ports that accommodated PC cards. The port made it possible to upgrade a laptop without opening the device, which was especially useful when an internal component stopped working or became obsolete.
The PC card was originally built around an enhanced 16-bit Industry Standard Architecture bus platform. It used a 68-pin, dual-row connecting interface and was similar in size to a standard credit card, but slightly thicker with more rounded corners. All PC cards were either 3.3-volt or 5-volt cards; the 3.3 V cards came with a protection feature that prevented use in a 5 V-only port. However, some cards could work in either 3.3 V or 5 V mode.
The card was based on standards published by the PCMCIA, an industry group set up in 1989 to promote standards for memory expansion cards and I/O integrated circuit cards. Because of the standards group's involvement, it was also known as a PCMCIA card. The PCMCIA Standard 2.1 was published in 1993 to provide assurance to PC users that peripheral devices that followed the standard would be compatible with their systems. The standard was most commonly applied to portable PCs, but it could also be used on desktop computers.
The PCMCIA standard allowed a maximum card length of 135.6 millimeters (mm) so that the PC card could extend outside the host and accommodate bulky devices such as batteries, oversized connectors, removable media, transceivers and antennas that some devices required.
Types of PC cards
Available in three types, the PC card offered data rates of up to 40 megabytes per second (MBps). All three versions of the PC card were similar in size to a credit card -- 85.6 mm (3.37 inches) long and 54.0 mm (2.13 inches) wide -- although their thickness varied, giving rise to different form factors.
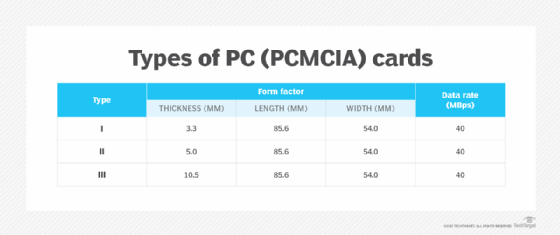
A Type I PC card occupied a single PC card slot and was mainly used for RAM or flash memory expansion. Type II cards added functionalities such as modems and network connections that were not already built into the laptop. These cards often came with a dongle or short wire with a full-size connector to provide a jack for connecting equipment to the device.
The Type I and Type II cards were mechanically compatible, which means a Type I card would work in a Type II slot. In addition, both these cards could work in a Type III slot. However, Type III cards would not work in Type I and II slots since these slots were meant for thinner cards. Also, Type III cards could accommodate connectors without a dongle.
Another type of PC card, the Type IV, was not officially recognized or standardized by the PCMCIA. It was introduced by Toshiba for use with its notebook computers and other machines. These devices featured a nonstandard, oversized slot to fit nonstandard, oversized PC cards with a thickness ranging from 14.5 mm to 16 mm.
A CableCard is a Type II PC card that allows U.S. consumers to view -- and record -- digital cable television channels. Roughly the size of a credit card, it can be used with compatible third-party devices such as PCs, TVs and DVRs to access TV services and cable content.
PC card vs. CardBus and ExpressCard
The PC card was eventually superseded by CardBus and ExpressCard, which offered data rates of up to 132 MBps and 342 MBps, respectively. Today, PC cards are no longer commonly used for memory expansion, although some portable computers do still use them for attaching peripheral devices such as network cards, modems and hard disk drives.
PC cards have been largely replaced by the ExpressCard interface. Unlike the PC card, the ExpressCard has a USB interface, and both its types have a standard thickness of 5 mm and length of 75 mm. Also, all modern-day laptop functions that the PC card interface was originally designed for are now powered by USB devices. The PCMCIA itself disbanded in 2009, turning over further development of ExpressCard to the USB Implementers Forum.
