STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics)
What is STEM?
STEM is an educational program developed to prepare primary and secondary students for college, graduate study and careers in the fields of science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). In addition to subject-specific learning, STEM aims to foster inquiring minds, logical reasoning and collaboration skills.
The goal of STEM programs is to increase the supply of qualified high-tech workers in the U.S., bolster innovation, improve the country's competitive position globally and strengthen economic growth. STEM gained importance in the early 2000s following the publication of several reports. One 2005 report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine entitled "Rising Above the Gathering Storm" emphasized the importance of science and technology jobs in fostering innovation, addressing societal problems and maintaining U.S. prosperity.
The Maryland State Department of Education developed a definition of STEM in 2012 that included the following seven standards of practice or skill necessary in a STEM program:
- learn and apply content
- integrate content
- interpret and communicate information
- engage in inquiry
- engage in logical reasoning
- collaborate as a team
- apply technology appropriately
Importance of STEM
STEM in higher education teaches students to think critically, prepares them for careers and creates professionals that can work across scientific disciplines to solve challenging problems.
STEM integrates multiple disciplines and trains students to use cross-disciplinary knowledge to solve problems. Additionally, STEM students take a rigorous and varied course load and develop a strong work ethic.
STEM programs promote a learn-by-doing approach. Students participate in real-world projects with real-world consequences. For example, students often participate in university research programs. This approach allows students to learn while also taking an active role in the development of emerging technology and groundbreaking research.
Universities hosting STEM programs benefit as well. They get credit for and revenue from new technologies the programs generate. For example, the University of Minnesota received $66 million from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to fund a program for antiviral drug development in 2022. The University was awarded this grant as a result of its innovative efforts in the initial response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Having workers with STEM skills boosts the U.S. economy and helps the country compete globally. To maintain an adequate STEM workforce, the U.S government offers programs to help immigrants with skills in STEM subjects obtain work visas.
Reasons to consider majoring in a STEM field
There are many reasons to consider a STEM major. The following are some of them:
- Challenging field of study. If students want an engaging field of study that challenges them, STEM is the way to go.
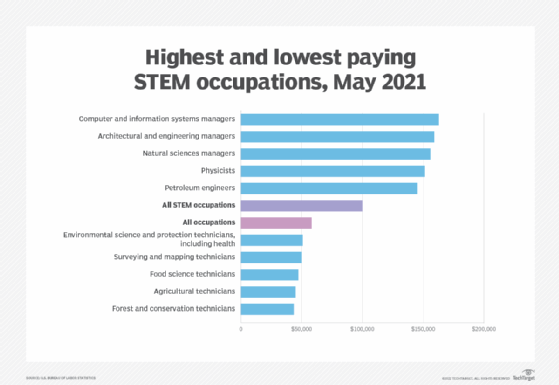
- Higher paying careers. STEM offers students a chance at higher paying jobs. In 2021, the Bureau of Labor Statistics found that STEM occupations had almost double the annual mean wage compared to the national average for all occupations.
- Make a difference. STEM gives students the tools to apply themselves to real-world problems and develop innovative solutions to those problems.
- Travel. STEM majors often have study abroad programs that enable students to travel, study and possibly work overseas.
- Job security. STEM skills are sought after in many occupations and can translate well across occupations. Most STEM majors require rigorous problem-solving and critical-thinking skills, which are useful in almost any occupation.
Examples of STEM majors
STEM major areas of study can be any college major in a scientific, technological, engineering or mathematical field. That said, individual colleges have different definitions of what counts as STEM in their curricula.
The following areas of study are typically STEM programs:
- computer science
- electronics and other technology-related disciplines
- engineering
- mathematics
- natural, physical and life sciences
The following majors are often included as STEM:
- accounting
- anthropology
- economics
- medicine
- nursing
- political science
- psychology
- social sciences
The U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) maintains a list of STEM majors, which it periodically updates. According to the DHS, a STEM field is one that is included in the Department of Education's Classification of Instructional Programs taxonomy, containing engineering, biological sciences, mathematics, physical sciences or a related field.
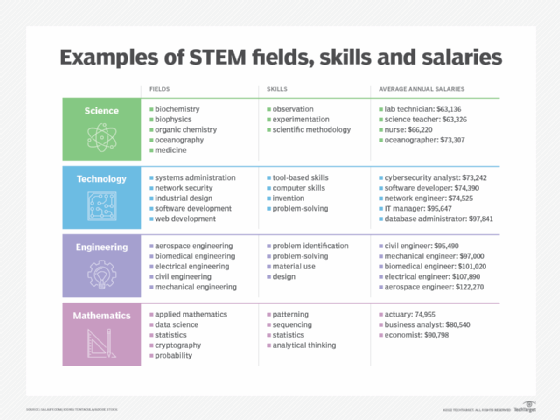
Top STEM careers
STEM majors are represented in every sector of the economy, including the private sector, nonprofits, and the government or miliary. These majors may lead to individuals earning advanced degrees and taking positions in management.
STEM majors often lead to jobs in fields where trained individuals are in high demand. They include careers in the following areas:
Computing
- computer systems analyst
- database administrator
- IT director
- network administrator
- software developer
Engineering
- audio engineer
- biomedical engineer
- civil engineer
- electrical engineer
- petroleum engineer
Physical science
- chemist
- cartographer
- agricultural technician
- physicist
- science teacher
Life sciences
- anesthetist
- clinical research associate
- oceanographer
- orthodontist
- science teacher
Mathematics
- accountant
- actuary
- economist
- financial analyst
- math teacher
- statistician
Data science is one of the many in-demand technology-centric fields that fall under the category of STEM. Learn 14 skills prospective data scientists must have to succeed in the field.
