business process
What is a business process?
A business process is an activity or set of activities that accomplish a specific organizational goal. Business processes should have purposeful goals, be as specific as possible and produce consistent outcomes.
Business process management (BPM) is a systematic approach to improving those processes, which helps organizations achieve their business goals. If an organization is unable to perform certain business processes internally due to cost or resource constraints, the company might use business process outsourcing. Many organizations contract specific business tasks -- such as payroll, human resources (HR) or accounting -- to a third-party service provider.
To measure the success of a business process, organizations track the completion of different steps within the process -- i.e., benchmarks -- or evaluate the quality of the process' endpoint. When an organization determines that a business process is not achieving the desired goals or outcomes, there are several strategies it can use for improvements. For example, an organization might opt to focus on business process visibility to identify issues in process performance or execution.
Organizations also engage in business process mapping to help boost the effectiveness of their business operations. Business process mapping provides a visual representation of how different processes function and gives organizations better visibility into how their business works.
Why are business processes important?
Defined business processes within the organization are critical to enterprise success for the following reasons:
- They help organizations identify and understand the actual work required to keep the lights on and to achieve organizational objectives.
- They break that work into organized, repeatable steps that workers can follow to achieve consistent outcomes.
- Using repeatable steps to produce consistent outcomes helps organizations to more accurately predict the resources they need, thereby lowering the risk of over or under provisioning valuable resources.
- The consistent, repeatable nature of defined business outcomes helps lower the risk of employees introducing workarounds or individualized steps that can cause disruptions, slow work and increase error rates.
- Being able to better measure the efficiency and effectiveness of the individual steps within the process enables teams to identify and mitigate inefficiencies and bottlenecks to improve performance; this is the foundation of continuous improvement.
- Teams are better able to identify where technologies -- such as robotic process automation (RPA) -- can be used to further boost effectiveness or efficiencies.
Business process vs. business procedure vs. business function
There are numerous concepts and corresponding terms to describe the art and science of running a business, with business process being only one of them. Business procedure and business function are two other frequently used terms.
Although similar sounding, they each describe different organizational ideas, as noted below:
A business process, as previously stated, is a series of related tasks that result in a desired output; it is an established set of repeatable activities.
A business procedure is a clearly stipulated way of undertaking a business process; it details the teams and individual workers responsible for each part of the process as well as the specifications applicable to performing and completing each of those parts.
A business function is an organizational unit within an enterprise or organization; each business function has its own specific set of responsibilities and activities that it must execute to support the business as it carries out its mission and overall objectives.
Although these terms all describe concepts required to operate an organization, they are not interchangeable.
Business process categories and examples
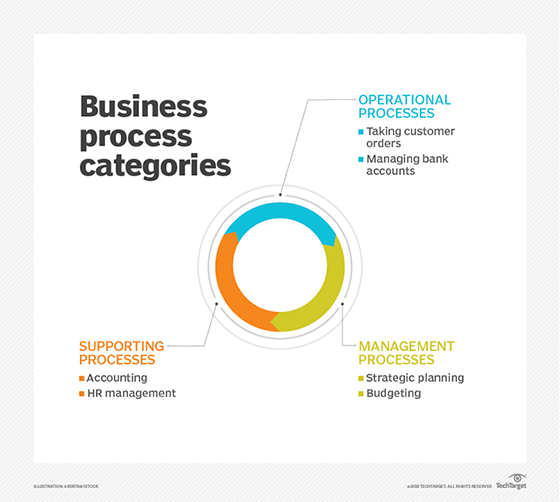
Business processes can be categorized into different buckets, with the most common three as follows:
- Operational processes. Also called primary processes, these processes deal with the core business and value chain and deliver value to the customer by helping to produce a product or service. Operational processes represent essential business activities that accomplish business objectives such as generating revenue. Examples of this include the following:
- taking customer orders
- processing product payments
- managing bank accounts
- Supporting processes. Also known as secondary processes, these involve back-office processes within the business functions that keep the organization running. One key difference between operational and supporting processes is that supporting processes do not directly provide value to customers. Examples of supporting processes include the following:
- accounting
- HR management
- workplace safety
- Management processes. These processes measure, monitor and control the activities related to business procedures and systems. Like supporting processes, management processes do not provide value directly to the customers. Some examples of management processes include the following:
- internal communications
- governance
- strategic planning
- budgeting
- infrastructure or capacity management
Some organizations and executives prefer to classify business processes by business function and group them under the following titles:
- accounting and finance business processes
- business development business processes
- HR management business processes
- marking and sales business processes
- product delivery business process
Business process management
Having established defined business processes, organizations should then engage in business process management.
BPM is at its core the discipline of studying and improving the business processes that exist within the enterprise. It typically involves first designing and implementing the processes and then doing the following:
- analyzing
- managing
- monitoring
- modeling
- redefining those existing processes
These activities help organizations oversee their existing processes to ensure they are operating smoothly and producing the intended outcomes. They also identify areas for improvement and help organizations implement changes to create better processes.
BPM also helps to identify tasks within processes that can be automated with technologies such as RPA or entire processes that are candidates for business process automation.
Organizations use BPM software to monitor and control automated and non-automated business processes and to help improve their existing processes.
BPM and the use of BPM software deliver numerous benefits by lowering the risks of the following:
- errors and bottlenecks that can disrupt the flow of processes;
- redundant activities within processes; and
- wasted resources.
They also help do the following:
- ensure good workflow management;
- minimize costs;
- create and maintain visibility into the processes;
- improve collaboration among teams that share processes or have business process handoffs;
- increase productivity;
- enable agility;
- ensure compliance; and
- boost efficiency.
Business process monitoring
One piece of BPM is business process monitoring. More specifically, business process monitoring is the measurement and analysis of process performance.
Organizations typically use analytics and monitoring software for this activity to track costs, key performance indicators and process cycle time as well as to detect errors and compliance issues.
Business process monitoring can also help improve business process visibility by identifying possible problems.
Organizations use functional monitoring to assess the functional performance of a process.
Technical monitoring helps measure the technical efficiency of an application by supervising and logging aspects such as response times and downtimes.
Business process visibility
Business process visibility provides the enterprise with a full view of each of its processes. This is important because organizations with good visibility into their processes can more quickly adjust business processes as market conditions and enterprise requirements change. Good business process visibility also helps management teams determine if their processes are still aligned with key business objectives and goals, and whether the accompanying procedures that help make a process successful are operating accurately. This in turn boosts operational responsiveness and expedites decision-making.
Business process modeling or mapping
Business processes are often depicted visually with a flow chart showing the sequence of required tasks and assigning certain benchmarks or decision points to each. Business process mapping or modeling illustrates pictorially, through graphs and charts, how certain processes flow into others.
Business process mapping and workflow can be thought of in the following ways:
- Sequential business process. This process is outlined on a document with clear start and endpoints. When following this process map, an organization performs a series of actions in order to complete a task within a predetermined timeline.
- Status-driven business process. This process does not have a strict start and endpoint. It can finish at any stage, depending on workflow changes, the nature of production or the office culture. Also, it is typical for a status-driven process to recur or cycle on the same step in the process.
- Parallel business process. When activities in a business process are executed in parallel, they are carried out simultaneously. In this type of business process execution, the activities on all the branches must be completed before the next step in the business process can commence.
History and evolution
The works of economist Adam Smith, academic and author Thomas Davenport, engineer Frederick Taylor and management guru Peter Drucker have significantly influenced how organizations define and handle business processes.
Smith, the author of The Wealth of Nations, first recognized how the use of labor division -- dividing work into a set of tasks performed by experts -- could lead to an increase in productivity.
Taylor's innovations in industrial engineering resulted in organizational productivity improvements. He is credited with transforming the workplace with his ideas on organizing work, task fragmentation and job measurement.
Drucker -- described as the father of modern management -- focused on the simplification and decentralization of processes and introduced the concept of outsourcing.
Davenport defined the business process as a set of logically related tasks performed to achieve a defined business outcome. According to Davenport, processes make up the structure that helps organizations complete the tasks required to produce value for its customers.
Learn how organizations are using business process automation to streamline their business operations and contain costs.






