
encryption
What is encryption?
Encryption is the method by which information is converted into secret code that hides the information's true meaning. The science of encrypting and decrypting information is called cryptography.
Encryption has long been used to protect sensitive information. Historically, it was used by militaries and governments. In modern times, encryption is used to protect data both at rest and in motion. At-rest data is the type stored on computers and storage devices. In-motion data refers to data in transit between devices and over networks.
Encryption is used in a variety of circumstances. Every time someone carries out a transaction on an ATM or buys something online with a smartphone, encryption protects the transmitted data. Businesses also rely on encryption to protect sensitive information from exposure in the event of a data breach or unauthorized individuals acquiring the data. Such exposure can have extensive financial implications and severely damage an organization's reputation.
Why is encryption important?
Encryption plays a vital role in securing different types of IT assets and personally identifiable information (PII). To this end, encryption serves four essential functions:
This article is part of
What is data security? The ultimate guide
- Confidentiality. Encodes the data to prevent it from being understood if it is intercepted.
- Authentication. Verifies the origin of the data that has been encrypted.
- Integrity. Validates that the data has not been altered since it was encrypted.
- Nonrepudiation. Prevents senders from denying they sent the encrypted data.
What are the benefits of encryption?
The primary purpose of encryption is to protect the confidentiality of digital data stored on computer systems or transmitted over the internet or other computer networks. It is used to safeguard a wide range of data, from PII to sensitive corporate assets to government and military secrets. By encrypting their data, organizations reduce the risk of exposing sensitive information, helping to avoid costly penalties, lengthy lawsuits, reduced revenue and tarnished reputations.
Many organizations use encryption not only to protect their data, but also to meet compliance regulations that require sensitive data to be encrypted. Encryption ensures that unauthorized third parties or threat actors cannot understand the data in the event they gain access to it. For example, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard requires merchants to encrypt customer payment card data both at rest and when transmitted across public networks.
What are the disadvantages of encryption?
Although encryption keeps unauthorized individuals from being able to understand sensitive data, encryption can also prevent the data's owners from being able to access their own information. If the encryption keys get lost or destroyed, the data owners might be permanently locked out of that data. Cybercriminals might also go after the encryption keys, rather than the data itself. Once they've acquired the keys, they can easily decipher the data.
Key management is one of the biggest challenges of building an enterprise encryption strategy because the keys to decrypt the ciphertext have to live somewhere in the environment, and attackers often have a good idea of where to look.
There are plenty of best practices for encryption key management, but they add extra layers of complexity to the backup and restoration processes. If a major disaster should strike, retrieving the keys and adding them to a new backup server could increase the time that it takes to get started with the recovery operation.
Having a key management system in place isn't enough. Administrators must also come up with a comprehensive plan for protecting the key management system. Typically, this means backing it up separately from everything else and storing those backups in a way that makes it easy to retrieve the keys in the event of a large-scale disaster.
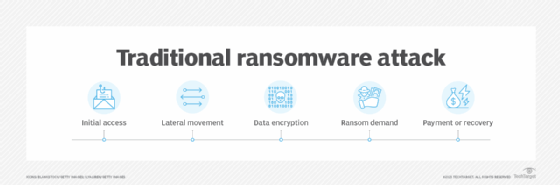
Another challenge with encryption is the fact that cybercriminals can also use it for their own purposes, which has led to an increasing number of ransomware attacks. In this scenario, the criminals gain access to the sensitive data, encrypt it with their own algorithms and then hold the data hostage until the victim organization comes up with the ransom, which can be quite steep.
How does encryption work?
An encryption system is made up of three major components: data, encryption engine and key manager. In application architectures, the three components usually run or are hosted in separate places to reduce the possibility that a single component is compromised and leads to the entire system being compromised. On a self-contained device, such as a laptop, all three components run on the same system.
When an encryption system is in place, the data is always in one of two states: unencrypted or encrypted. Unencrypted data is also known as plaintext, and encrypted data is called ciphertext. Encryption algorithms, or ciphers, are used to encode and decode the data. An encryption algorithm is a mathematical method for encoding data according to a specific set of rules and logic.
During the encryption process, the encryption engine uses an encryption algorithm to encode the data. A number of algorithms are available, differing in complexity and levels of protection. The engine also uses an encryption key in conjunction with the algorithm to ensure that the ciphertext that is output is unique. An encryption key is a randomly generated string of bits that are specific to the algorithm.
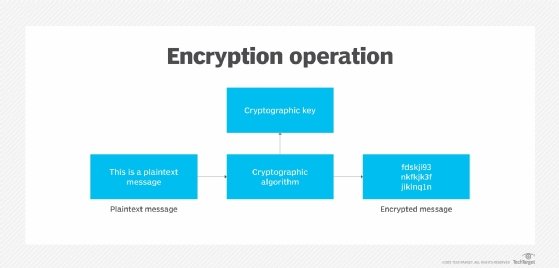
After the data is converted from plaintext to ciphertext, it can be decoded only through the use of the proper key. This key might be the same one used for encoding the data or a different one, depending on the type of algorithm -- symmetric or asymmetric. If it's a different key, it's often called a decryption key.
When encrypted data is intercepted by an unauthorized entity, the intruder has to guess which cipher was used to encrypt the data and what key is required to decrypt the data. The time and difficulty of guessing this information is what makes encryption such a valuable security tool. The more extensive the encryption algorithm and key, the more difficult it becomes to decrypt the data.
What are the two types of encryption?
When setting up a system for encrypting data, a security team must determine which encryption algorithm to use to encode the data. Before doing that, however, the team should first decide on the type of algorithm. The two most common types are symmetric and asymmetric:
- Symmetric ciphers. Also referred to as secret key cyphers, these algorithms use a single key for both encrypting and decrypting data. The key is sometimes referred to as a shared secret because the sender or computing system doing the encryption must share the secret key with all entities authorized to decrypt the message. Symmetric key encryption is usually much faster than asymmetric encryption. The most widely used symmetric key cipher is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which was designed to protect government-classified information.
- Asymmetric ciphers. Also known as public key encryption, these types of algorithms use two different -- but logically linked -- keys for encrypting and decrypting data. Asymmetric cryptography often uses prime numbers to create keys since it is computationally difficult to factor large prime numbers and reverse-engineer the encryption. The Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption algorithm is currently the most widely used public key algorithm. With RSA, the public or the private key can be used to encrypt a message; whichever key is not used for encryption becomes the decryption key.
Today, many cryptographic processes use a symmetric algorithm to encrypt data and an asymmetric algorithm to securely exchange the secret key.
Encryption key management and wrapping
Encryption is an effective way to secure data, but the cryptographic keys must be carefully managed to ensure data remains protected yet accessible when needed. Access to encryption keys should be monitored and limited to those individuals who absolutely need to use them.
Organizations should have strategies in place for managing encryption keys throughout their lifecycle and protecting them from theft, loss or misuse. This process should begin with an audit that determines how the organization currently configures, controls, monitors and manages access to its keys.
Key management software can help centralize key management, as well as protect keys from unauthorized access, substitution or modification.
Key wrapping is a type of security feature found in some key management software suites that essentially encrypts an organization's encryption keys, either individually or in bulk. The process of decrypting keys that have been wrapped is called unwrapping. Key wrapping and unwrapping activities are usually carried out with symmetric encryption.
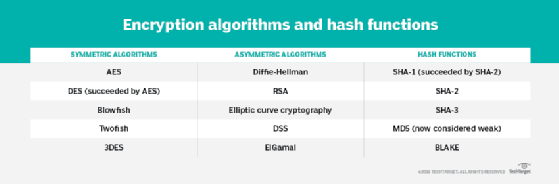
Encryption algorithms
A variety of symmetric and asymmetric ciphers are available for encrypting data. The algorithms vary in their complexity and the exact approach they take to protecting data. The following ciphers are some of the more common algorithms that have been used over the years:
- AES. A symmetric block cipher chosen by the U.S. government to protect classified information. It is implemented in software and hardware throughout the world to encrypt sensitive data. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) started development of AES in 1997 when it announced the need for a successor algorithm for the Data Encryption Standard (DES), which was starting to become vulnerable to brute-force attacks.
- DES. An outdated symmetric key method of data encryption. DES works by using the same key to encrypt and decrypt a message so both the sender and the receiver must know and use the same private key. DES has been superseded by the more secure AES algorithm.
- Diffie-Hellman key exchange. A symmetric algorithm that uses numbers raised to specific powers to produce decryption keys on the basis of components that are never directly transmitted, making the task of a would-be code breaker mathematically overwhelming. The Diffie-Hellman key exchange is also called the exponential key exchange.
- Elliptical curve cryptography (ECC). An asymmetric cipher that uses algebraic functions to generate security between key pairs. The resulting cryptographic algorithms can be faster and more efficient and can produce comparable levels of security with shorter cryptographic keys. This makes ECC algorithms a good choice for internet of things (IoT) devices and other products with limited computing resources.
- Quantum key distribution (QKD). Available as both a symmetric cipher and semisymmetric cypher. The QKD algorithm is a method for encrypting data with the aid of quantum mechanics. The encryption keys are generated by using a pair of entangled photons that are then transmitted separately from the data. Quantum entanglement enables the sender and receiver to know whether the encryption key has been intercepted or changed before the transmission even arrives. This is because, in the quantum realm, the act of observing the transmitted information changes it. Once it has been determined that the encryption is secure and has not been intercepted, permission is given to transmit the encrypted message over a public internet channel.
- RSA. Asymmetric cypher that was first publicly described in 1977 by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. British mathematician Clifford Cocks created a public key algorithm in 1973, but the U.K.'s Government Communications Headquarters kept it classified until 1997. Many protocols, such as Secure Shell (SSH), OpenPGP, Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions, and Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (TLS) -- rely on RSA for encryption and digital signature functions.
- Twofish. A symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits and variable-length key of size 128, 192 or 256 bits. Optimized for 32-bit central processing units, the algorithm is open source and available for free. Twofish stands out from other encryption algorithms by its use of the S-box, a pre-computed, key-dependent substitution box. The S-box obscures the relationship between the key and the ciphertext, although it still depends on the cipher key to decrypt the data.
The security provided by encryption is directly tied to the type of cipher used to encrypt the data, as well as to the strength of the decryption keys used to convert the ciphertext to plaintext. In the United States, cryptographic algorithms approved under NIST's Federal Information Processing Standards should be used whenever cryptographic services are required.
Implementing encryption
Organizations take a variety of approaches to encrypting data. The methods they use depend on their environments, the type of data, the levels of protection they're trying to achieve and other variables. Here are some of the strategies that they use when implementing encryptions:
- Bring your own encryption (BYOE) is a cloud computing security model that enables cloud service customers to use their own encryption software and manage their own encryption keys. BYOE is also referred to as bring your own key. BYOE works by enabling customers to deploy a virtualized instance of their own encryption software alongside the business application they are hosting in the cloud.
- Cloud storage encryption is a service offered by cloud storage providers whereby data or text is transformed using encryption algorithms and is then placed in cloud storage. Cloud encryption is almost identical to in-house encryption with one important difference: The cloud customer must take time to learn about the provider's policies and procedures for encryption and encryption key management to match encryption with the level of sensitivity of the data being stored.
- Column-level encryption is an approach to database encryption in which the information in every cell in a particular column has the same password for access, reading and writing purposes.
- Deniable encryption is a type of cryptography that enables encrypted data to be decrypted in two or more ways, depending on which decryption key is used. Deniable encryption is sometimes used for misinformation purposes when the sender anticipates, or even encourages, interception of a communication.
- Encryption as a service is a subscription model that enables cloud service customers to take advantage of the security that encryption offers. This approach provides customers who lack the resources to manage encryption themselves with a way to address regulatory compliance concerns and protect data in a multi-tenant environment. Cloud encryption offerings typically include full-disk encryption (FDE), database encryption or file encryption.
- End-to-end encryption (E2EE) guarantees data being sent between two parties cannot be viewed by an attacker that intercepts the communication channel. Use of an encrypted communication circuit, as provided by TLS between web client and web server software, is not always enough to ensure E2EE; typically, the content being transmitted is encrypted by client software before being passed to a web client and decrypted only by the recipient. Messaging apps that provide E2EE include Meta's WhatsApp and Signal. Facebook Messenger users may also get E2EE messaging with the Secret Conversations option.
- FDE is encryption at the hardware level. FDE works by automatically encrypting data on a storage drive into a form that cannot be understood by anyone who doesn't have the key to undo the conversion. Without the proper authentication key, even if the drive is removed and placed in another machine, the data remains inaccessible. FDE can be installed on a computing device at the time of manufacturing, or it can be added later on by installing special software.
- Field-level encryption is the ability to encrypt data in specific fields on a webpage. Examples of fields that can be encrypted are credit card numbers, Social Security numbers, bank account numbers, health-related information, wages and financial data. Once a field is chosen, all the data in that field is automatically encrypted.
- Homomorphic encryption is the conversion of data into ciphertext that can be analyzed and worked with as if it were still in its original form. The homomorphic encryption approach enables complex mathematical operations to be performed on encrypted data without compromising the encryption.
- HTTPS enables website encryption by running HTTP over the TLS protocol. To enable a web server to encrypt all content that it sends, a public key certificate must be installed.
- Link-level encryption encrypts data when it leaves the host; decrypts it at the next link, which may be a host or a relay point; and then reencrypts it before sending it to the next link. Each link may use a different key or even a different algorithm for data encryption, and the process is repeated until the data reaches the recipient.
- Network-level encryption applies cryptoservices at the network transport layer -- above the data link level but below the application level. Network encryption is implemented through IP Security, a set of open Internet Engineering Task Force standards that, when used in conjunction, create a framework for private communication over IP networks.
- Quantum cryptography depends on the quantum mechanical properties of particles to protect data. In particular, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle posits that the two identifying properties of a particle -- its location and its momentum -- cannot be measured without changing the values of those properties. As a result, quantum-encoded data cannot be copied because any attempt to access the encoded data changes the data. Likewise, any attempt to copy or access the data causes a change in the data, thus notifying the authorized parties to the encryption that an attack has occurred.
Cryptographic hash functions
Hash functions provide another type of encryption. Hashing is the transformation of a string of characters into a fixed-length value or key that represents the original string. When data is protected by a cryptographic hash function, even the slightest change to the message can be detected because it makes a big change to the resulting hash.
Hash functions are considered to be a type of one-way encryption because keys are not shared and the information required to reverse the encryption does not exist in the output. To be effective, a hash function should have the following characteristics:
- Computationally efficient. Easy to calculate.
- Deterministic. Reliably produces the same result.
- Preimage-resistant. Output that does not reveal anything about input.
- Collision-resistant. Extremely unlikely that two instances produce the same result.
Popular hashing algorithms include Secure Hash Algorithms and Message Digest Algorithm 5.
How to break encryption
For any cipher, the most basic method of attack is brute force -- trying each possible decryption key until the right one is found. The length of the key determines the number of possible keys, hence the feasibility of this type of attack. Encryption strength is directly tied to key size, but as the key size increases, so too do the resources required to perform the computation.
Alternative methods of breaking encryptions include side-channel attacks, which don't attack the actual cipher. Instead, they measure or exploit the indirect effects of its implementation, such as an error in execution or system design.
Attackers may also attempt to break a targeted cipher through cryptanalysis, the process of attempting to find a weakness in the cipher that can be exploited with a complexity less than a brute-force attack. The challenge of successfully attacking a cipher is easier if the cipher itself is already flawed.
For example, there have been suspicions that interference from the National Security Agency (NSA) weakened the DES algorithm. Following revelations from former NSA analyst and contractor Edward Snowden, many believe the NSA has attempted to subvert other cryptography standards and weaken encryption products.
Encryption backdoors
An encryption backdoor is a way to get around a system's authentication or encryption. Governments and law enforcement officials around the world, particularly in the Five Eyes (FVEY) intelligence alliance, continue to push for encryption backdoors, which they claim are necessary in the interests of national safety and security as criminals and terrorists increasingly communicate via encrypted online services.
According to the FVEY governments, the widening gap between the ability of law enforcement to lawfully access data and their ability to acquire and use the content of that data is "a pressing international concern" that requires "urgent, sustained attention and informed discussion."
Opponents of encryption backdoors have said repeatedly that government-mandated weaknesses in encryption systems put the privacy and security of everyone at risk because the same backdoors can be exploited by hackers.
Law enforcement agencies, such as the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), have criticized technology companies that offer E2EE, arguing that such encryption prevents law enforcement from accessing data and communications even with a warrant. The FBI has referred to this issue as "going dark," while the U.S. Department of Justice has proclaimed the need for "responsible encryption" that can be unlocked by technology companies under a court order.
Australia, one of the FVEY members, passed legislation that allows Australian Border Force (ABF) officers to search and seize electronic devices without any type of warrant. Although travelers entering the country aren't required to provide their passcodes or offer assistance to access their devices, the ABF has the right to confiscate those devices.
Threats to IoT, mobile devices
By 2019, cybersecurity threats increasingly included those on IoT and mobile computing devices. According to Kaspersky's Securelist, 97.91% of password brute-force attempts targeted Telnet in the first half of 2023. Telnet is an unencrypted text protocol widely used on IoT devices. Securelist also reported that Kaspersky products blocked 438,962 malicious installation packages on mobile devices. Of these packages, 21,674 were related to mobile banking Trojans, and 1,855 were mobile ransomware Trojans.
Meanwhile, NIST has encouraged the creation of cryptographic algorithms suitable for use in constrained environments, including mobile and IoT devices. In a first round of judging in April 2019, NIST chose 56 lightweight cryptographic algorithms candidates to be considered for standardization. Since then, NIST has conducted a second round and then a final round. From the 10 finalists, the NIST Lightweight Cryptography Team selected the Ascon family for standardizing lightweight cryptography applications.
History of encryption
The word encryption comes from the Greek word kryptos, meaning hidden or secret. The use of encryption is nearly as old as the art of communication itself. As early as 1900 B.C., an Egyptian scribe used nonstandard hieroglyphs to hide the meaning of an inscription.
In a time when most people couldn't read, simply writing a message was often enough, but encryption schemes soon developed to convert messages into unreadable groups of figures to protect the message's secrecy while it was carried from one place to another. The contents of a message were reordered (transposition) or replaced (substitution) with other characters, symbols, numbers or pictures in order to conceal its meaning.
In 700 B.C., Spartans wrote sensitive messages on strips of leather wrapped around sticks. When the tape was unwound, the characters became meaningless, but with a stick of exactly the same diameter, the recipient could recreate (decipher) the message.
Later, Romans used what's known as the Caesar shift cipher, a monoalphabetic cipher in which each letter is shifted by an agreed number. So, for example, if the agreed number is three, then the message "Be at the gates at six" becomes "eh dw wkh jdwhv dw vla." At first glance, this may look difficult to decipher, but juxtaposing the start of the alphabet until the letters make sense doesn't take long. Also, the vowels and other commonly used letters, like t and s, can be quickly deduced using frequency analysis, and that information, in turn, can be used to decipher the rest of the message.
The Middle Ages saw the emergence of polyalphabetic substitution, which uses multiple substitution alphabets to limit the use of frequency analysis to crack a cipher. This method of encrypting messages remained popular, despite many implementations that failed to adequately conceal when the substitution changed -- also known as key progression. Possibly the most famous implementation of a polyalphabetic substitution cipher is the Enigma electromechanical rotor cipher machine used by Germans during World War II.
It was not until the mid-1970s that encryption took a major leap forward. Until this point, all encryption schemes used the same secret for encrypting and decrypting a message: a symmetric key.
Encryption was almost exclusively used only by governments and large enterprises until the late 1970s when the Diffie-Hellman key exchange and RSA algorithms were first published and the first PCs were introduced.
In 1976, Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman's paper, "New Directions in Cryptography," solved one of the fundamental problems of cryptography: how to securely distribute the encryption key to those who need it. This breakthrough was followed shortly afterward by RSA, an implementation of public key cryptography using asymmetric algorithms, which ushered in a new era of encryption. By the mid-1990s, both public key and private key encryption were being routinely deployed in web browsers and servers to protect sensitive data.
See how to use a public key and private key in digital signatures and how to use centralized encryption methods in large-scale IT environments. Explore our comprehensive guide to data security. Learn how encryption is implemented in hardware through the use of hardware security modules.






