control system
What is a control system?
A control system is a set of mechanical or electronic devices that regulates other devices or systems by way of control loops. Typically, control systems are computerized.
Control systems are a central part of production and distribution in many industries. Automation technology plays a big role in these systems. The types of control loops that regulate these processes include industrial control systems, such as supervisory control and data acquisition, systems and distributed control systems.
How are control systems used?
Control systems are used to enhance production, efficiency and safety in many industries:
- Agriculture.
- Chemical plants.
- Pulp and paper mills.
- Industrial and manufacturing quality control.
- Boiler controls and power plant operations.
- Environmental control.
- Water and sewage treatment plants.
- Food and food processing.
- Metal and mines.
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Sugar refining.
The following are specific examples of where control systems are used in industrial processes:
- Boiler controls in heating and power plant systems.
- Pipeline monitoring.
- Water distribution systems.
- Wastewater treatment systems.
- Electricity distribution systems.
What are the main types of control systems?
There are two types of control systems commonly used: open-loop and closed-loop systems.
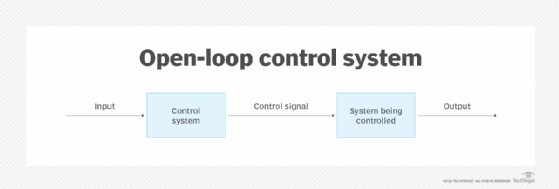
Open loop
These control systems operate with human input. The control action is independent of the output. In household use, a washing machine is an example of an open-loop system because someone needs to make selections among the settings for it runs. A time-based traffic light system is an industrial example of an open-loop control system, where traffic engineers must decide the timing for the stop, go and caution lights.
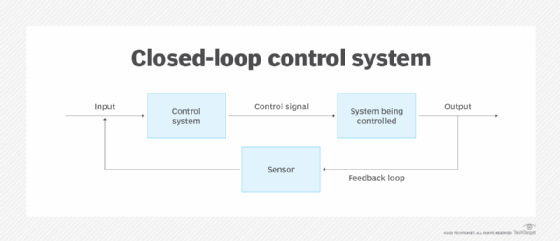
Closed loop
These systems can be actively managed or set to operate autonomously. They use feedback signals from the system to provide automatic control and maintain specific settings or a desired state without human intervention. Some control loops can be switched between closed and open modes. When open, a switchable loop is manually controlled; when closed, it can be fully automated.
A thermostat is an example of a closed-loop system. It turns a heating system on and off based on signals it receives from sensors that monitor air temperature. Temperature control is a particularly important part of maintaining a proper data center environment.
In Figure 2, the technician manages a system that can be remotely controlled. The technician regularly sends input signals to the device, and it sends output signals via a feedback loop and a sensor that monitors the device. When the sensor receives an error signal from the device, it sends an alert message over the feedback loop to the technician, who then sends instructions to the device as needed to counter the negative feedback.
Figure 2 also depicts a feedback control system. The control system needs feedback data to control the device.
What is control system made up of?
The control loops that make up the overall system generally include a sensor, a controller and a final control element. The sensor reads the process variable or a related process control measurement. The controller receives the signal from the sensor and forwards it to the instrumentation, the remote terminal units and the final control elements. There, the process variable is adjusted to be kept constant at the chosen set point.
Other components in control loop modules include programmable logic controllers, programmable automation controllers, remote terminal units, control servers and intelligent electronic devices.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of control systems?
Closed-loop control systems are widely used in many applications. They are effective in controlling externally located devices, providing dependable and readily available output data while also withstanding external disruptions.
However, control systems are complex, and require training and documentation for optimum operation and to achieve the desired output. Malfunctions to remote sensors can provide inaccurate data on system performance, possibly resulting in unnecessary system changes. Their complexity also means they aren't necessarily ready to use out of the box and might require programming and other prelaunch activities before using.
Learn about how oil, energy and chemical companies are replacing expensive control systems with cheaper, more secure ones.
