coulomb (C)
What is a coulomb (C)?
A coulomb (C) is the standard unit of electric charge in the International System of Units (SI). It is the amount of electricity that a 1-ampere (A) current carries in one second (s). A quantity of 1 C is equal to the electrical charge of approximately 6.24 x 1018 electrons or protons. This comes to about 6.24 quintillion particles.
In the SI standard, the coulomb is considered a derived unit, which means it is constructed from one or more of the seven base units, in this case, ampere and second. Prior to 2018, the base units provided the foundation for the SI standard, and the derived units were constructed from these. Now, the standard is built upon seven defining constants, and all base and derived units can be constructed directly from those constants. However, the SI standard has retained the concept of base and derived units because they are so well established.
One of the seven foundational constants is the elementary charge, which is the electric charge carried by a single electron or proton. The elementary charge (e) is 1.602176634 ⋅ 10-19 C. Both electrons and protons carry the same amount of charge. However, a proton carries a positive charge, and an electron carries a negative charge. So, the elementary charge can be positive (+e) or negative (-e).
By fixing the elementary charge at 1.602176634 ⋅ 10-19 C, the standard fixes the coulomb at a specific number of electrons or protons that make up 1 C of charge. The following formula can be used to calculate that number:
Q = n ⋅ e
The symbol Q represents the amount of charge in coulombs, and the symbol n refers to the number of electrons or protons. If both sides of the equation are divided by e, the number of particles in a coulomb can be calculated as the following:
Q = n ⋅ e
Q / e = (n ⋅ e) / e
n = Q / e (after reversing Q / e = n)
n = 1 C / (1.602176634 ⋅ 10-19 C)
n = 6.24150907 ⋅ 1018 C
In the fourth line, 1 C replaces Q because the objective is to find the number of particles in a single coulomb, and the elementary charge constant replaces the e. Based on this calculation, 1 C contains the charge of approximately 6.24 ⋅ 1018 particles, a number that would look something like this:
6,241,509,070,000,000,000
In terms of SI base units, 1 C is the equivalent of 1 ampere-second, which can be expressed as 1 C = 1 A ⋅ 1 s (or C = A ⋅ s). This can also be thought of as an ampere being equal to 1 coulomb divided by 1 s, as in 1 A = 1 C / 1 s (or A = C / s). In other words, if a current in a circuit is 1 A, 1 C of charge passes through a point in the circuit every second.
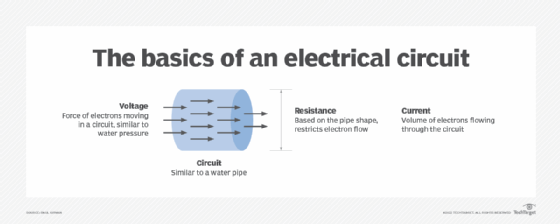
How does an ampere compare to a coulomb?
The ampere is the SI standard of electric current. This is in contrast to the coulomb, which is the SI standard of electric charge. One ampere is equal to the electric current that corresponds to the flow of 1 / (1.602176634 ⋅ 10-19) elementary charges per second. Before the SI was updated in 2018, the ampere was based on the force between two current-carrying conductors with a fixed value of vacuum magnetic permeability at 4π ⋅ 10−7 henries per meter.
The force with which two electrically charged bodies attract or repel one another depends on the product of their charges in coulombs, as well as on the distance between them. If the polarities are the same -- negative/negative or positive/positive -- the coulomb force is repulsive; if the polarities are opposite -- negative/positive or positive/negative -- the force is attractive. For any two charged bodies, the coulomb force decreases in proportion to the square of the distance between their charge centers.
See also: resistance, Ohm's law, reactance, admittance, susceptance and henry.
