address space
What is address space?
Address space is the amount of memory allocated for all possible addresses for a computational entity -- for example, a device, a file, a server or a networked computer. The system provides each device and process address space that holds a specific portion of the processor's address space. This can include either physical or virtual addresses accessible to a processor or reserved for a particular process.
The width of its address bus and registers often restricts the processor's address space. However, a memory management technique called virtual memory can increase the size of the address space to be higher than that of the physical memory.
Address space is classified as either flat or segmented. Flat address spaces are represented by incrementally increasing integers starting at zero. Independent segments augmented by offsets or values added to create secondary addresses represent segmented addresses.
In some systems, address space can be converted from one format to another through a thunking process -- low-level, machine-generated code used to deploy details of a software system. Thunking is often used to delay calculations until the system requires a result.
Some types of address spaces
Here are a few examples of address spaces.
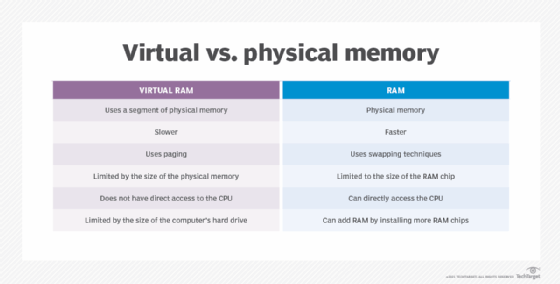
Virtual address space
A binary number in the virtual memory that allows processes to use a location in primary storage is a virtual address. This accommodates use of the main memory, independent of other processes, and supports the use of more space than what actually exists. It works by relegating some content to a hard disk or internal flash drive.
Logical address space
A logical address space is a set of logical addresses a computer generates for a specific program. A group of physical addresses mapped to corresponding logical addresses is called a physical address space.
IPv4 to IPv6
In terms of IP address space, concern emerged that the 32-bit address space of IP version 4 (IPv4) would be inadequate to support the enormous growth of the internet. So, IPv6 was developed with its 128-bit address space.
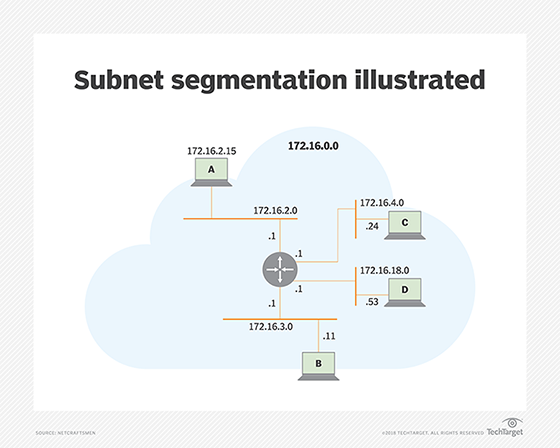
Subnetting IPv6 address space
The primary purpose of subnetting IPv6 address space is to improve address allocation efficiency by subnetting a segment of a network address space. Splitting an extensive network into smaller groups of interconnected networks reduces traffic, which helps increase network speeds because traffic does not have to flow through unnecessary routes. The subnet mask shares the network portion of the IP address and the host address range with the computer. The host address range comprises addresses assigned to host computers on the network.
Address space layout randomization
Address space layout randomization is a memory security mechanism used to prevent potential exploitation of memory corruption vulnerabilities. Adding randomness into a process's virtual memory address space makes it challenging to exploit vulnerabilities.
Address space in Microsoft Azure
The address space for a virtual network in Microsoft Azure comprises one or more addresses that do not overlap. Classless Inter-Domain Routing notations specify these address ranges and define them as public or private. When creating a virtual network, the custom private IP address space is specified using both public and private addresses. Azure then assigns resources, including a private IP address, from the address space you set in a virtual network.
Address space vs. memory space
The addresses programmers use are called virtual addresses. A set of these virtual addresses is called address space.
The place where the address was saved in the main memory is known as the location. A group of locations is called memory space.
Address space translation
Address space translation describes the process of concentrating the frame number with the offset part of a logical address. This approach helps form a physical address.
The page table base register holds the base address for the page table of the current process. This is essentially a processor register the operating system manages.
Explore IP subnetting and how to make computational storage work in your applications. Also, see the difference between static and dynamic IP addresses and MAC addresses and IP addresses.







