mail server (mail transfer/transport agent, MTA, mail router, internet mailer)
What is a mail server?
A mail server -- also known as a mail transfer agent, or MTA; mail transport agent; mail router; or internet mailer -- is an application that receives incoming email from local users and remote senders and forwards outgoing messages for delivery. A computer dedicated to running these applications is also called a mail server. Microsoft Exchange, Exim and Sendmail are common examples of mail server programs.
A mail server works with other programs to create a messaging system. A messaging system includes all the applications necessary to keep email moving smoothly. When an email is sent, a program, such as Microsoft Outlook, forwards the message to a mail server. The mail server then forwards the message to either another mail server or to a holding area on the same server to be forwarded later.
What are the types of mail servers?
Mail servers can be divided into two categories: incoming mail servers and outgoing mail servers.
An incoming mail server stores mail and sends it to a user's inbox. Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3) and Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) are the two main types of incoming mail servers.
POP3, for example, downloads email from a server and stores incoming email messages on a single device until the user opens the email client. Once the user downloads the email, it is automatically deleted from the server, unless the "keep mail on server" setting is enabled. Many internet service providers offer their users POP3 email accounts, as they are more space efficient.
IMAP servers enable users to preview, delete and organize emails before transferring them to multiple devices from the email server. Copies of emails are left on the server until the user deletes them.
An outgoing mail server operates by having a user's machine communicate with Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), which handles the email delivery process. SMTP servers work with other types of mail servers, namely POP3 or IMAP, to send emails from email clients.
What is the process of sending an email?
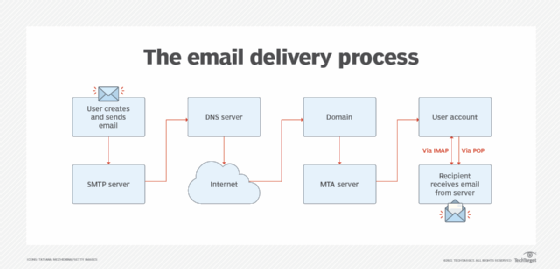
The following steps show the general process of sending an email:
- The user composes an email using a third-party email client, such as Outlook, and hits Send.
- The email client connects to the SMTP server.
- The SMTP server identifies and processes the recipient's email address, the body of the message and additional attachments.
- If the domain name is the same as the sender's, the message is routed directly over POP3 or IMAP. If the domain name is different, the SMTP server communicates with the domain name system (DNS) to find the recipient's server. The DNS translates the recipient's email domain name into an Internet Protocol (IP) address.
- The recipient's IP address connects to the SMTP server. Once the IP is identified, the sent message is routed between unrelated SMTP servers until it arrives at its destination.
- The recipient's SMTP server handles the email. It checks the message and directs it over to an IMAP or POP3 server. The email is then placed in a mail queue until the recipient retrieves it.
On-premises vs. cloud mail servers
Email servers can be located on premises or be cloud-based. On-premises servers are physical servers that are at an organization's location. The organization must manage and maintain all servers and infrastructure. Cloud-based servers are virtual and are hosted using cloud computing. There is no one right option for every organization, as it depends on the business.
On-premises mail servers use the organization's servers, receiving all emails and sending them to an indexed database. On-premises servers typically require a larger upfront investment for hardware, installation and management. The potential for scalability is also less immediate compared to email servers hosted in the cloud. The organization is responsible for providing security.
Cloud-based email servers, such as Amazon Simple Email Service (SES), operate the same way as on-premises servers, but the data is stored in a cloud environment that a separate vendor provides. There is typically a monthly fee included, set up as a pay-as-you-go pricing method. Scaling is usually easier and more immediate compared to on-premises servers since an organization is just using more of the vendor's resources instead of having to add more physical server space. The cloud vendor provides security.
Considerations for choosing a mail server
An organization must take the following into account before choosing a mail server:
- Security. Email services should use advanced tools to protect information. Other features an email provider may provide include encryption, antimalware, spam filtering and data loss prevention tools.
- Cost. On-premises email servers cost more upfront but also provide more fine-grained control over systems and security. Cloud-based email services typically have less upfront cost and require less maintenance.
- Archiving and storage. Ensure a vendor offers sufficient storage for email archiving. Some services may also offer an option to move old messages to an archive automatically.
- Compatibility. Email services may also offer options to sync with web-based and mobile applications, such as email, calendar and contact applications.
What are examples of mail servers?
There are many different free and paid mail servers that use SMTP. Some examples are the following:
- Amazon SES is a cloud-based platform with an SMTP interface.
- Halon MTA is an email operations and security platform that uses SMTP.
- Microsoft Exchange Server is a paid email, calendaring, contact, scheduling and collaboration platform that is deployed on the Windows Server operating system.
- OpenSMTPD is a free MTA developed as part of the OpenBSD
- Open-Xchange is a free web-based collaboration and office productivity software suite with email and scheduling capabilities.
- Oracle Beehive is a paid collaboration platform that combines email, instant messaging and conferencing.
How to find mail server information
If users are trying to add their email account to another mail app, they may need the POP, IMAP or SMTP server settings. Gaining access to mail server information differs by platform.
Microsoft Outlook for PC
- To view and enable POP access in Outlook.com, go to Settings and View all Outlook settings.
- Click on Mail and Sync email.
- POP and IMAP settings appear here with the option to enable them.
Apple Mail for macOS
- Open Mail, select Preferences and Accounts.
- Select Server Settings.
- Select the Account pop-up menu and SMTP Server List.
iPhone (iOS 14)
- Go to Settings, tap Mail and Accounts.
- Select the corresponding email.
- Under the account is the Outgoing Mail Server and under that is SMTP. Select to view Primary and other SMTP servers.
Android devices (Android 11)
- Open Settings.
- Click on Apps.
- Select Email settings.
- Under Accounts, click on your email address.
- Under Advanced settings, click on Server settings.
- The screen shows the incoming and outgoing server information.
Learn more about SMTP and important email security protocols in this article.
