multiprogramming
What is multiprogramming?
Multiprogramming is a rudimentary form of parallel processing in which several programs run at the same time on a uniprocessor system. However, because there is only one processor, there is no true simultaneous execution of different programs. Instead, the operating system (OS) executes part of one program, then part of another, and so on. In this sense, multiprogramming can be thought of as pseudo-parallelism. To the user, it appears that multiple programs are executing at the same time, but that is not what is happening.
Prior to the introduction of multiprogramming, single processor computers could run only one program at a time. Once the program was launched, it ran to completion, unless it was interrupted or the application ceded control. Only after the first program finished running could the processor execute the next program in the queue. This meant that the CPU sat idle during I/O operations, even if other programs were waiting, resulting in application delays and underutilized processor resources.
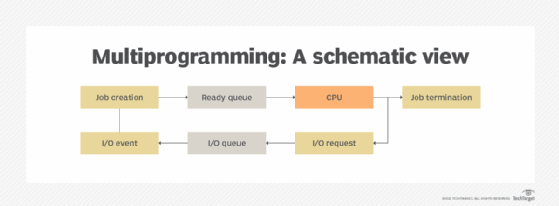
Multiprogramming addresses this issue by allowing multiple programs to load into memory and run each one in rotation as CPU resources become available. For example, when Program A starts, the operating system assigns CPU resources to that program until the program launches into its I/O operations. Then, the OS assigns CPU resources to Program B, which is already loaded into memory. If Program B launches into I/O operations and Program A is still running its I/O operations, the OS will assign CPU resources to Program C; otherwise, it will assign them back to Program A.
The operating system is responsible for ensuring that CPU resources are properly allocated and reallocated to each program as resources become available, working around the various program's I/O operations. To achieve this, the OS uses a technique called context switching, which ensures that a program's state is preserved in memory and can be readily accessed as the OS switches between programs and CPU assignments.
Types of multiprogramming
Multiprogramming is implemented in one of two ways: cooperative multiprogramming or preemptive multiprogramming.
Cooperative multiprogramming is the older of the two models and is seldom used today. With cooperative multiprogramming, context switching is initiated by the programs themselves rather than the OS. Processor resources are reassigned only when a program releases control of those resources. The operating system has no choice but to execute a program with the expectation, but not the certainty, that the program will eventually return control to the OS.
The problem with this approach is that a program can monopolize CPU resources for an inordinate amount of time, keeping other programs waiting. Even worse, a buggy or malicious program might launch an infinite loop and never give up control of the CPU, resulting in a locked system or system crash. Not only does this disrupt user and application workflows, but it can be difficult to debug because it might not be obvious which of several programs is at fault.
With preemptive multiprogramming, the OS has complete control over context switching. It allocates CPU resources based on queued programs and their I/O operations, while limiting the time each program can run. So, if there is a problem with one of the programs, it cannot interfere with operations indefinitely. Today, most computers use preemptive multiprogramming.
See also: multiprocessing
