search engine
What is a search engine?
A search engine is a coordinated set of programs that searches for and identifies items in a database that match specified criteria. Search engines are used to access information on the World Wide Web.
How do search engines work?
Google is the most commonly used internet search engine. Google search takes place in the following three stages:
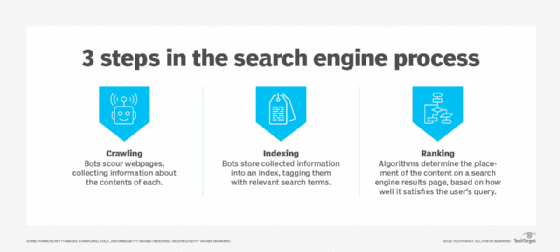
- Crawling. Crawlers discover what pages exist on the web. A search engine constantly looks for new and updated pages to add to its list of known pages. This is referred to as URL discovery. Once a page is discovered, the crawler examines its content. The search engine uses an algorithm to choose which pages to crawl and how often.
- Indexing. After a page is crawled, the textual content is processed, analyzed and tagged with attributes and metadata that help the search engine understand what the content is about. This also enables the search engine to weed out duplicate pages and collect signals about the content, such as the country or region the page is local to and the usability of the page.
- Searching and ranking. When a user enters a query, the search engine searches the index for matching pages and returns the results that appear the most relevant on the search engine results page (SERP). The engine ranks content on a number of factors, such as the authoritativeness of a page, back links to the page and keywords a page contains.
Specialized content search engines are more selective about the parts of the web they crawl and index. For example, Creative Commons Search is a search engine for content shared explicitly for reuse under Creative Commons license. This search engine only looks for that specific type of content.
Country-specific search engines may prioritize websites presented in the native language of the country over English websites. Individual websites, such as large corporate sites, may use a search engine to index and retrieve only content from that company's site. Some of the major search engine companies license or sell their search engines for use on individual sites.
How search engines rank results
Not every search engine ranks content the same way, but some have similar ranking algorithms. Google search and other search engines like it rank relevant results based on the following criteria:
- Query meaning. The search engine looks at user queries to establish searcher intent, which is the specific type of information the user is looking for. Search engines use language models to do this. Language models are algorithms that read user input, understand what it means and determine the type of information that a user is looking for.
- Relevance. Keywords from search queries are matched to keywords in content. Keywords that appear in several places in the content signify more relevance than others.
- Quality. Search engines look for indicators of expertise, authority and trustworthiness in the content. If other prominent websites link to the content, it is considered more trustworthy.
- Usability. Search engines evaluate the accessibility and general user experience of content and reward content with better page experience. One example of page usability is mobile-friendliness, which is a measure of how easy a webpage is to use on a mobile device.
- User data. A user's past search history, search settings and location data are a few of the data types search engines use to determine the content rankings they choose.
Search engines might use other website performance metrics, such as bounce rate and time spent on page, to determine where websites rank on a results page. Search engines might return different results for the same term searched as text-based content versus an image or video search.
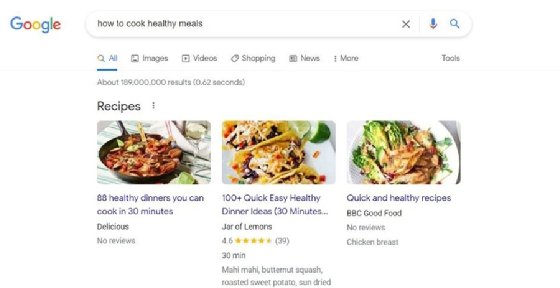
Content creators use search engine optimization (SEO) to take advantage of the above processes. Optimizing the content on a page for search engines increases its visibility to searchers and its ranking on the SERP. For example, a content creator could insert keywords relevant to a given search query to improve results for that query. If the content creator wants people searching for dogs to land on their page, they might add the keywords bone, leash and hound. They might also include links to pages that Google deems authoritative.
What is the goal of search engines?
The primary goal of a search engine is to help people search for and find information. Search engines are designed to provide people with the right information based on a set of criteria, such as quality and relevance.
Webpage and website providers use search engines to make money and to collect data, such as clickstream data, about searchers. These are secondary goals that require users to trust that the content they are getting on a SERP is enough to engage with it. Users must see the information they're getting is the right information.
User trust can be earned in different ways, including the following:
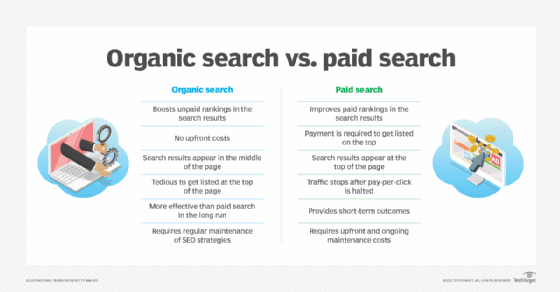
- Organic results. Unpaid organic results are seen as more trustworthy than paid, ad-based results.
- Authority. Google seeks to establish a webpage's authority to identify it as the source of true information.
- Privacy. DuckDuckGo is a search engine that uses privacy protection to establish trust. It protects user privacy and avoids skewed search results that can come from using personal information to target users or place them in limited search categories, known as filter bubbles.
How do search engines make money?
Search engines make money in several ways, including the following:
- Pay-per-click ads. Advertisers or third-party advertising networks place ads on SERPs and on the content itself. The more views or clicks a search-related keyword gets, the more advertisers pay to have their advertisements associated with it.
- User data. Search engines also make money from the user data that they collect. Examples include search history and location data. This data is used to create a digital profile for a given searcher, which search engine providers can use to serve targeted ads to that user.
- Contextual ads. Search engines also capitalize on serving up contextual ads that are directly related to the user's current search. If a search engine includes a shopping feature on the platform, it might display contextual ads for products related to the user's search in the sidebar of a website where advertisements are displayed. For example, if the online store sells books, an ad may appear in the corner of the page for reading glasses.
- Donations. Some search engines are designed help nonprofits solicit donations.
- Affiliate links. Some engines include affiliate links, where the search engine has a partnership in which the partner pays the search engine when a user clicks the partner's link.
How do search engines personalize results?
Search engines personalize results based on digital searcher profiles created from user data. User data is collected from the application or device a user accesses the search engine with. User data collected includes the following:
- search history
- search date and time
- location information
- audio data
- user ID
- device identification
- IP address
- device diagnostic data
- contact lists
- purchase history
Cookies are used to track browsing history and other data. They are small text files sent from the websites a user visits to their web browser. Search engines use cookies to track user preferences and personalize results and ads. They are able to remember settings, such as passwords, language preferences, content filters, how many results per page and session information.
Using private browsing settings or incognito browsing protects users from tracking but only at the device level. Search history and other information accumulated during search is not saved and is deleted after the search session. However, internet service providers, employers and the domain owners of the websites visited are able to track digital information left behind during a search.
Popular search engines
Google is the most popular search engine, capturing over 92% of the search engine market share worldwide, according to web traffic analysis service StatCounter. Yahoo and Microsoft Bing come in second and third with nearly 4% and just over 1% of the market, respectively.
DuckDuckGo has gained some popularity because of its focus on protecting users' private search data. Some users may prefer to use Bing or Yahoo for their other integrated offerings.
Other popular search engines in the world are the following:
- Baidu
- BoardReader
- Brave Search
- Creative Commons Search
- Ecosia
- Ekoru
- Gibiru
- Gigablast
- GiveWater
- Haystak
- Mojeek
- MetaGer
- Naver
- OneSearch
- Onion Search
- Recon
- Search Encrypt
- SearX
- Sentient Hyper-Optimized Data Access Network (Shodan)
- Startpage
- Swisscows
- Qwant
- Wiki.com
- Wolfram Alpha
- Yandex
Some of these engines, such as Ecosia and Startpage, use their own crawlers but rely on larger, more mainstream search engines, like Google and Bing, for indexing. Others, such as Mojeek, use their own crawlers and maintain their own index.
Alternative search engines, like HaystakOnion Search and Recon, let users browse the dark web using the Tor browser, which encrypts user traffic for added privacy and security. The dark web is a hidden part of the internet not accessible by traditional browsers.
Other search engines focus on specific information types. For instance, Wolfram Alpha is an internet search engine for science and math topics. Shodan is a search tool for internet-connected devices.
Browsers generally have a default search engine. For example, Google Chrome and Safari for iOS use Google.
The future of search engines
Search engines and the companies that develop them are likely to use new technologies to improve the accuracy, relevance and quality of the answers search engines provide. They'll also use advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, to improve user experience in the future. For example, a user might someday be able to upload a picture of a computer to Google, ask "Is this a good computer for gaming?" and get a thoughtful, nuanced answer.
Google is likely to continue to retain the majority of the search market. Given that, SEO companies can expect Google to keep updating its core search engine algorithm periodically. Google does this to keep those companies from optimizing content for a specific algorithm.
However, more niche engines might emerge in the future to provide the specificity and privacy that many users perceive Google lacks. Users may gravitate to search tools that provide enhanced privacy or better quality by only indexing a portion of the internet.
Some experts also believe that search engine use is declining because more information seeking will happen on other applications and social media sites, such as Facebook, TikTok and LinkedIn, in the future.
Although Google keeps its algorithm a secret, content creators can have some control over content performance. Learn ways to improve your search engine ranking.
