social media
What is social media?
Social media is a collective term for websites and applications that focus on communication, community-based input, interaction, content-sharing and collaboration.
People use social media to stay in touch and interact with friends, family and various communities. Businesses use social applications to market and promote their products and track customer concerns.
Business-to-consumer websites include social components, such as comment fields for users. Various tools help businesses track, measure and analyze the attention the company gets from social media, including brand perception and customer insight.
Social media has enormous traction globally. Mobile applications make these platforms easily accessible. Some popular examples of general social media platforms include Twitter, Facebook and LinkedIn.
What are the business applications of social media?
In business, social media is used to market products, promote brands, connect to customers and foster new business. As a communication platform, social media promotes customer feedback and makes it easy for customers to share their experiences with a company. Businesses can respond quickly to positive and negative feedback, address customer problems and maintain or rebuild customer confidence.
Social media is also used for crowdsourcing. That's the practice of using social networking to gather knowledge, goods or services. Companies use crowdsourcing to get ideas from employees, customers and the general public for improving products or developing future products or services.
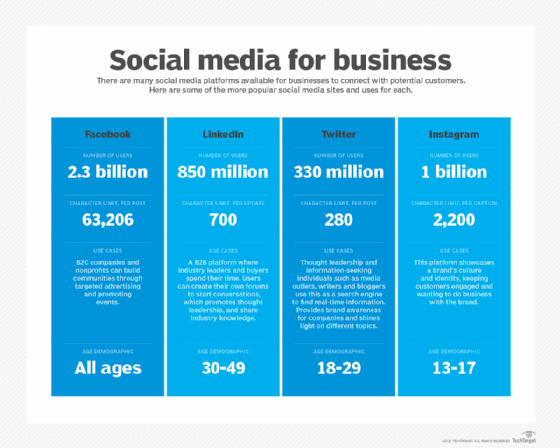
Examples of business to business (B2B) applications include the following:
- Social media analytics. This is the practice of gathering and analyzing data from blogs and social media websites to assist in making business decisions. The most common use of social media analytics is to do customer sentiment analysis.
- Social media marketing (SMM). This application increases a company's brand exposure and customer reach. The goal is to create compelling content that social media users will share with their social networks. A key components of SMM is social media optimization (SMO). Like search engine optimization, SMO is a strategy for drawing new visitors to a website. Social media links and share buttons are added to content and activities are promoted via status updates, tweets and blogs.
- Social customer relationship marketing. Social CRM is a powerful business tool. For example, a Facebook page lets people who like a company's brand to like the business's page. This, in turn, creates ways to communicate, market and network. Social media sites give users the option to follow conversations about a product or brand to get real-time market data and feedback.
- Recruiting. Social recruiting has become a key part of employee recruitment strategies. It is a fast way to reach a lot of potential candidates, both active job seekers and people who were not thinking about a job change until they say the recruitment post.
- Enterprise social networking. Businesses also use Enterprise social networking to connect people who share similar interests or activities. These applications include internal intranets and collaboration tools, such as Yammer, Slack and Microsoft Teams, that give employees access to information and communication capabilities. Externally, public social media platforms let organizations stay close to customers and make it easy to conduct market research.
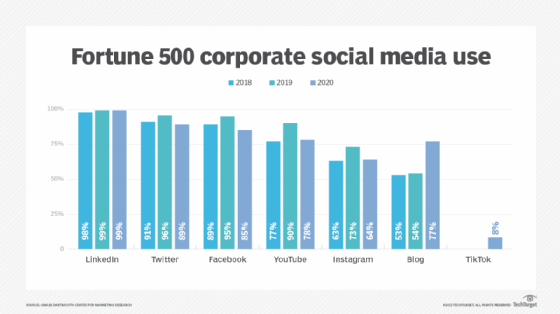
What are the benefits of social media?
Social media provides several benefits, including the following:
- User visibility. Social platforms let people easily communicate and exchange ideas or content.
- Business and product marketing. These platforms enable businesses to quickly publicize their products and services to a broad audience. Businesses can also use social media to maintain a following and test new markets. In some cases, the content created on social media is the product.
- Audience building. Social media helps entrepreneurs and artists build an audience for their work. In some cases, social media has eliminated the need for a distributor, because anyone can upload their content and transact business online. For example, an amateur musician can post a song on Facebook, get instant visibility among their network of friends, who in turn share it on their networks.
What are the challenges of social media?
Social media can also pose challenges to individual users, in the following ways:
- Mental health issues. Overuse of social apps can result in burnout, social media addiction and other issues.
- Polarization. Individuals can end up in filter bubbles. They create the illusion of open discourse when the user is actually sequestered in an algorithmically generated online community.
- Disinformation. Polarized environments foster the spread of disinformation where the perpetrator's intent is to deceive others with false information.
Businesses face similar and unique social media challenges.
- Offensive posts. Conversations on intranets and enterprise collaboration tools can veer off into non-work-related subjects. When that happens, there is potential for co-workers to disagree or be offended. Controlling such conversations and filtering for offensive content can be difficult.
- Security and retention. Traditional data security and retention policies may not work with the features available in collaboration tools. This can raise security risks and compliance issues that companies must deal with.
- Productivity concerns. Social interaction, whether online or in person, is distracting and can affect employees' productivity.
What are enterprise social media best practices?
It is important for companies to have a social media strategy and establish social media goals. These help to build trust, educate their target audience and create brand awareness. They also enable real people to find and learn about a business.
Here are some social media social media best practices for companies to follow:
- Establish social media policies that set expectations for appropriate employee social behavior. These policies should also ensure social media posts do not expose the company to legal problems or public embarrassment. Guidelines should include directives for when an employee must identify them self as a company representative and rules for what type of information can be shared.
- Focus on platforms geared to B2B marketing, such as Twitter and LinkedIn.
- Put in place an engaging, customer-centric strategy in social media campaigns. An example would be to use Twitter to field questions from customers.
- Include rich media, such as pictures and video, in content to make it more compelling and appealing to users.
- Use social media analytics tools to measure user engagement with content and to keep on top of trends.
- Use a conversational voice in posts that comes across as professional but not rigid.
- Shorten long form content to make it social friendly. Lists and audio and video snippets are examples.
- Embrace employees and customers talking positively about the organization and repost that content.
- Check in on analytics and management tools frequently, if not on a daily basis, as well as the social media accounts.
What are the different types of social media?
The four main categories of social platforms are these:
- Social networks. People use these networks to connect with one another and share information, thoughts and ideas. The focus of these networks is usually on the user. User profiles help participants identify other users with common interests or concerns. Facebook and LinkedIn are good examples.
- Media-sharing networks. These networks focus is on content. For example, on Youtube, interaction is around videos that users create. Other media-sharing networks are TikTok and Instagram. Streaming platforms like Twitch are considered a subset of this category.
- Community-based networks. The focus of this type of social network is in-depth discussion, much like a blog forum. Users leave prompts for discussion that spiral into detailed comment threads. Communities often form around select topics. Reddit is an example of a community-based network.
- Review board networks. With these networks, the focus is on a review, usually of a product or service. For example, on Yelp, users can write reviews on restaurants and endorse each other's reviews to boost visibility.
What are examples of social media?
Here are some examples of popular web-based social media platforms:
- Facebook is a free social networking website where registered users create profiles, upload photos and video, send messages and keep in touch with friends, family and colleagues.
- LinkedIn is a social networking site designed for the business community. Registered members can create networks of people they know and trust professionally.
- Pinterest is a social curation website for sharing and categorizing images found online. The main focus of Pinterest is visual, though it does call for brief descriptions of images. Clicking on an image will take a user to the original source. For example, clicking on a picture of a pair of shoes might redirect a user to a purchasing site; an image of blueberry pancakes might redirect to the recipe.
- Reddit is a social news website and forum where site members curate and promote stories. The site is composed of hundreds of sub-communities called subreddits. Each subreddit has a specific topic, such as technology, politics or music. Reddit site members, also known as "redditors," submit content that members vote on. The goal is to elevate well-regarded stories to the top of the site's main thread page.
- Twitter is a free microblogging service for registered members to broadcast short posts called tweets. Twitter members can broadcast tweets and follow other active users' tweets using several platforms and devices.
- Wikipedia is a free, open content encyclopedia created through a collaborative community. Anyone registered on Wikipedia can create an article for publication; registration is not required to edit articles.
The takeaway
Social media is everywhere. Individuals and businesses of all sizes and types use it. It's a critical resource for engaging with customers, getting customer feedback and expanding company visibility.
An effective social strategy can enhance an organization's reputation and build trust and awareness among a growing network of connections. While some are more tailored to B2B promotion, no platforms are off limits.