solid
What is a solid?
A solid is a state of matter that retains its shape and density when not confined.
What is a solid state?
When particles are arranged and packed closely -- compared to those in a gas or liquid -- and are relatively stable, they are considered to be in a solid state. Solids tend to have a rigid shape, as the atoms or molecules of matter in the solid state are generally compressed and tightly connected through chemical bonds. These bonds can produce an amorphous shape or a regular lattice.
In electronics, solid state refers to components and systems based entirely on semiconductor materials, such as silicon, germanium or gallium arsenide. Transistors and diodes -- the most common solid-state devices -- are often combined with resistors, capacitors and other components to create integrated circuits (ICs). All electronic systems incorporate ICs and, therefore, transistors.

The 4 states of matter
There are four states of matter:
Examples of solids are the following:
- bricks and other building materials, like concrete, wood and glass;
- dry ice or frozen carbon dioxide;
- ice;
- most metals;
- most minerals;
- rocks; and
- salt.
When a solid is heated, the atoms or molecules gain kinetic energy. If the Temperature becomes sufficiently high, this kinetic energy overcomes the forces that hold the atoms or molecules in place.
Then, the solid may become a liquid or a gas. For example, when ice is heated gradually, it goes from the solid (ice) to the liquid state (water). When water is heated, it can change state from liquid (water) to gas (steam).
What are the different classes of solids?
There are two classes of solids: crystalline and amorphous. Made up of crystals, crystalline solids tend to fracture along defined surfaces that have a characteristic shape, depending on the arrangement and forces among the atoms or molecules in them. Amorphous solids, however, lack any apparent crystalline structure.
Crystalline solids boast an organized and highly ordered microscopic structure with constituent atoms, ions or molecules. Known as a crystal lattice, this microscopic structure extends uniformly through all points within the crystalline solid.
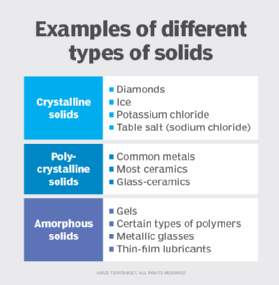
Examples of crystalline solids are the following:
- diamonds
- ice
- potassium chloride
- table salt (sodium chloride)
To classify a crystalline solid, use the characteristic forces exerted by different types of chemical bonds that join together with other particles to form a solid. For example, strong ionic bonds are usually the result of crystalline structures that can separate to form ions in water. The sharing of valence electrons helps form covalent bonds and is often found in organic compounds.
There are four types of crystalline solids:
- Ionic solids. Ionic solids do not have distinct molecules, but the ions present are held together by ionic bonds. Table salt is an example of an ionic solid. It consists of a sodium ion and a chloride ion.
- Metallic solids. In metallic solids, the metal atoms are held together through metallic bonds, and the electrons can freely move around within the solid. This is why metals are malleable and have good conductivity.
- Covalent network solids. The atoms in a covalent network solid are held together by covalent bonds. These covalent bonds form a continuous network. Examples of covalent network solids include diamonds, graphite and quartz.
- Molecular solids. As the name implies, molecular solids consist of molecules in a particular pattern. There are somewhat weak intermolecular forces holding the molecules together. Ice is an example of a molecular solid.
What are polycrystalline solids?
In nature, crystalline solids rarely appear in their pure form. Most often, they are found as polycrystalline solids. When tiny grains of crystals, known as crystallites, join together and form a large structure, it is called a polycrystalline solid. The size of each grain can vary from nanometers to millimeters, and the grains are separated by grain boundaries and usually have random crystallographic orientations.
Examples of polycrystalline solids are the following:
- common metals
- most ceramics
- glass-ceramics
What are amorphous solids?
By contrast, amorphous, or noncrystalline, solids lack long-range order in the organization of their constituent atoms, ions or molecules. Amorphous solids have interconnected structural blocks of solids in their internal structure and a higher solubility than crystalline solids.
Examples of amorphous solids are the following:
- gels
- certain types of polymers
- metallic glasses
- thin-film lubricants
See also: table of physical units, matter, compound, proton, neutron, dielectric material and conductor.
