sound card
What is a sound card?
A sound card is a computer component responsible for generating and recording audio. It enables users to connect analog speakers, headphones and microphones to their computer. Most modern computers have a built-in sound card in the motherboard.
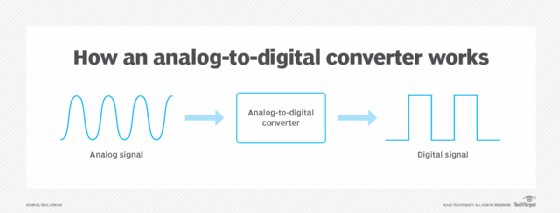
Generating audio on computers is challenging because sound is fundamentally analog, while computers are digital devices. Moreover, the human ear is incredibly sensitive to even the slightest changes in sound. The sound card's primary function is to convert digital signals into analog output for speakers and headphones. It also converts signals from microphones to digital input.
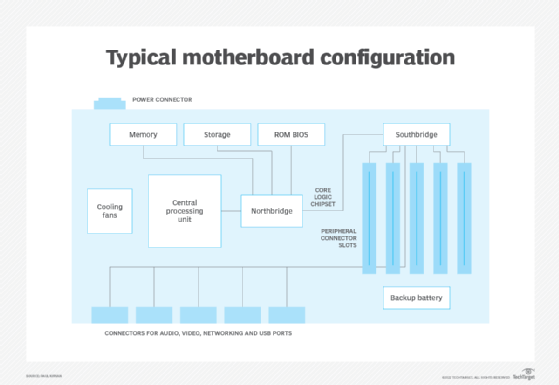
How do sound cards work?
A sound card operates through a digital-analog-converter (DAC) and an analog-digital-converter (ADC) and uses dedicated chips to lessen the CPU load. A preamplifier (preamp) boosts signal levels and controls volume. It may also be able to perform audio processing, such as audio equalization.
Sound cards used to be expansion cards for early computers, often with ISA or PCI slots. Newer cards use PCIe. However, as audio recording and playback became ubiquitous, and the cost of components decreased, it became common to incorporate basic sound card functionality into the motherboard. Although most computers no longer have physical sound cards, the term "sound card" still refers to the chips and functionality that provide audio output.
At the very least, a sound card provides a 3.5 mm stereo audio out and audio in TRS (tip, ring, sleeve) jack. However, many modern devices now use a single 3.5 mm TRRS (tip, ring, ring, sleeve) jack that combines both the headphone and microphone into a single port. Advanced sound cards offer additional input and output jacks. These may have additional 3.5 mm jacks for 5.1 or 7.1 channel surround sound, digital outputs or a digital optical audio port. Older sound cards may also have a MIDI or joystick port.
External sound cards are typically called audio interfaces, and they usually connect over USB. Advanced sound production and recording require an audio interface with multiple independent audio inputs and outputs. They may also have specialized ports such as XLR.
As technology continues to evolve, computers increasingly provide digital audio output. In such cases, HDMI and Bluetooth connections are digital-only and do not require a sound card. Instead, an external device such as a TV or Bluetooth headphones perform digital-to-analog conversion. However, basic sound cards will still be included in most computers because analog speakers and headphones remain widespread.
Sound card color code
The 3.5 mm jacks are color-coded so users can easily tell which port is for which channel. These colors include the following:
- Pink. Microphone input.
- Light blue. Line level input.
- Lime green. Left and right stereo output or headphones.
- Orange. Center and subwoofer output.
- Black. Surround sound left and right output.
- Grey. Surround sound rear left and right output.
- Yellow. Digital output.
Learn the essentials of buying server hardware, including what you need to know about server motherboards.
